Are you concerned about the growing National Debt and its impact on the economy? Explore the causes behind government borrowing, its effects on taxes, public spending, and economic growth, and discover strategies to address this pressing issue. Gain a deeper understanding of how the National influences your financial future and what actions you can take to stay informed. Start learning today and make sense of the numbers that shape our economy!
What the National Debt Means to You

The National Debt isn’t just an abstract figure, it’s a critical factor that affects your financial life in many ways. It influences the economy at large, shaping interest rates, inflation, tax policies, and government spending on essential services like education, healthcare, and infrastructure. A rising National Debt can lead to higher taxes or reduced public services, impacting your daily life and financial opportunities. For businesses, it affects borrowing costs and economic growth. For individuals, it determines future economic stability and the financial burden on upcoming generations.
Understanding the National Debt is vital for making informed decisions about your finances and advocating for policies that secure economic stability. Learn how government borrowing works, why it matters, and how it could shape your future. Empower yourself with knowledge and join the conversation about managing the debt to create a more stable economy for everyone.
See now:
The Importance of Interest Rate Forecasting In Trading
Planning To Measure The PMI For Your Successful Trading
What is a Contractionary Policy? Tools Used for Policies
Why is National Debt Important?

National Debt is more than just a financial figure—it’s a critical component of a nation’s economic health. Understanding its importance helps to reveal how it influences key aspects of everyday life, including:
- Economic Stability: A manageable National Debt can support investments in infrastructure, education, and innovation, driving economic growth. However, excessive debt may lead to inflation or economic downturns.
- Interest Rates: High debt levels can push up interest rates, making borrowing more expensive for businesses and individuals, which can slow economic activity.
- Tax Policies: To manage debt, governments may need to raise taxes or reduce public services, directly affecting citizens’ disposable income and access to essential programs.
- Global Confidence: A nation with unsustainable debt risks losing the confidence of global investors, potentially leading to economic crises.
The Structure of National Debt
The structure of National Debt refers to how a government organizes and manages its borrowing, including who it owes money to, the types of debt issued, and the timeline for repayment. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
Domestic vs. Foreign Debt
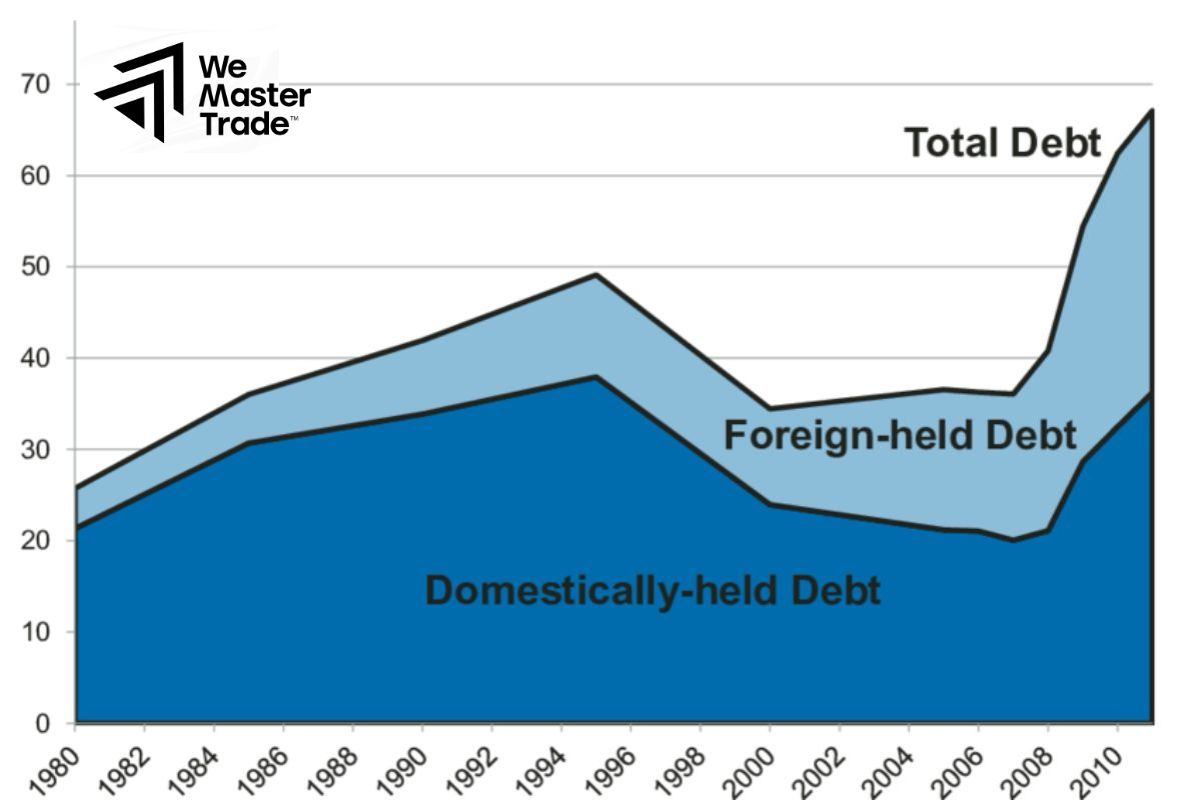
- Domestic Debt: Borrowed from within the country, often through bonds sold to citizens, banks, or institutions.
- Foreign Debt: Borrowed from other countries or international organizations, such as the IMF or World Bank. This type of debt depends on foreign currency and global market conditions.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Debt
- Short-Term Debt: Obligations that must be repaid within a year. It provides quick funding but can increase rollover risks.
- Long-Term Debt: Loans or bonds that mature over several years, offering stability and predictability for repayment schedules.
Creditors
- Public Sector: Includes pension funds and other government-owned entities.
- Private Sector: Banks, corporations, and individual investors.
- Foreign Investors: Other countries, international banks, and global institutions.
The Effects of National Debt
Here’s a closer look at its effects:
Economic Growth

- Positive Impact: Borrowing to fund infrastructure, education, or technological advancements can stimulate economic growth.
- Negative Impact: High debt levels can crowd out private investment as the government competes for capital, slowing long-term growth.
Interest Rates
- High levels of debt can increase demand for borrowing, driving up interest rates.
- Rising interest rates make loans more expensive for businesses and individuals, potentially slowing consumer spending and investment.
Inflation and Currency Value
- When financed through excessive money printing, debt can lead to inflation, eroding purchasing power.
- Large foreign debt can weaken the national currency if investors lose confidence, making imports more expensive.
Global Investor Confidence
- A well-managed debt portfolio can attract foreign investment, boosting the economy.
- However, excessive debt levels may reduce investor confidence, leading to lower credit ratings and higher borrowing costs.
Comparing National Debts of Countries
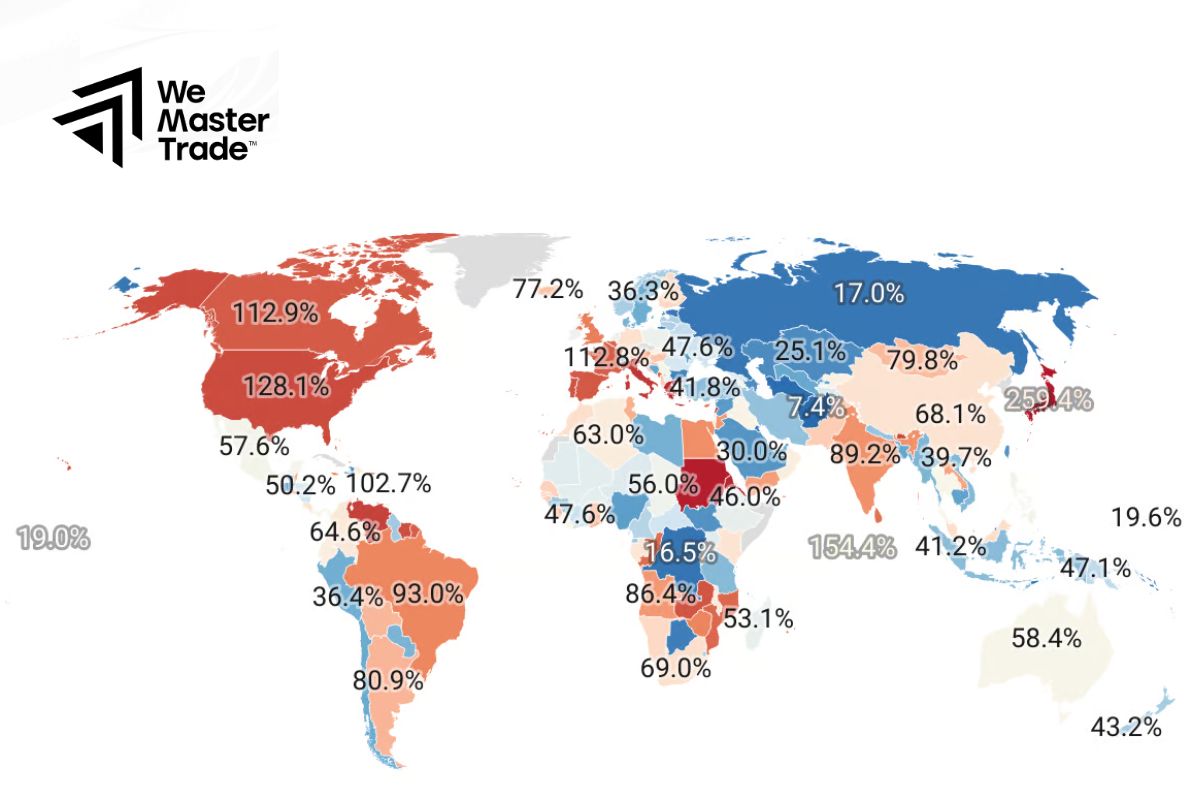
Here is a comparison table of national debts of different countries, including factors such as total national debt, debt-to-GDP ratio, and debt sustainability.
| Country | Total National Debt (in trillion USD) | Debt-to-GDP Ratio | Comments |
| USA | >30,000 | ~120% | High debt, but supported by the USD as the global reserve currency. |
| Japan | >10,000 | >250% | Very high debt, but manageable due to high savings rate and domestic debt. |
| China | >10,000 | ~70% | Significant debt but strong economic growth and good control over domestic debt. |
| Greece | >400 | >150% | High debt, struggling to maintain due to political and economic challenges. |
| Italy | >2,500 | >150% | Large debt, but supported within the EU framework. |
| India | ~1,700 | ~90% | Moderate debt, facing challenges with foreign debt management. |
| Australia | ~600 | ~45% | Low debt, easily manageable due to a stable economy. |
FAQs about National Debt
Is National Debt Always Bad?
No, it’s not always bad. Debt can finance growth-promoting projects, but excessive debt can strain the economy and reduce essential services.
Who is Responsible for Paying the National Debt?
The government pays the debt, but taxpayers ultimately cover the cost through taxes.
How Does National Debt Affect Future Generations?
Future generations may face higher taxes or cuts in services to repay debt, but if the debt funds productive investments, it can benefit them economically.
Does High National Debt Lead to Financial Crisis?
Not necessarily. While high debt increases risk, it depends on how well it’s managed. Excessive debt can cause instability, but strong economies can handle higher debt levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, National Debt is a complex issue that, when managed properly, can support economic growth and development. However, excessive debt can lead to financial instability and affect future generations. If you’re interested in learning more about how national impacts economies or need advice on financial management, don’t hesitate to explore our resources or contact us today. Stay informed and take control of your financial future!
See more:
What is the Trade Balance? How to Calculate Balance Trading
Understanding Monetary Policy? Common Types of Policy
Apply The Labor Market Reports Effectively In Forex Trading
Understand The Importance Of Fiscal Policy In Trading Market











