Explore the world of Monetary Policy and its crucial role in shaping economic stability. Understand how central banks use tools like interest rates and money supply to control inflation, boost employment, and maintain growth. Dive deeper into its strategies and real-world impacts to enhance your knowledge. Click here to stay ahead in understanding the forces that drive the economy!
What is Monetary Policy?
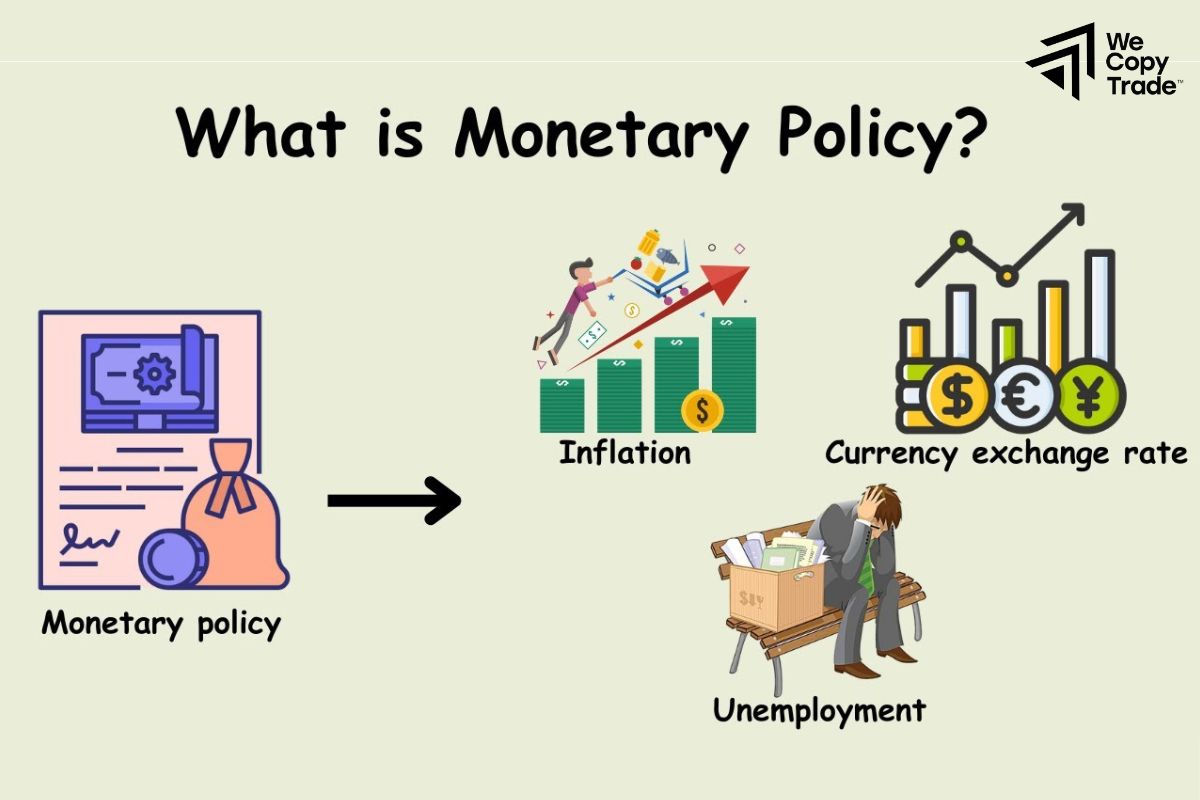
Monetary Policy refers to the strategies and actions undertaken by a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, or others, to manage a country’s money supply, interest rates, and overall economic stability. Its primary objectives typically include controlling inflation, fostering employment, stabilizing the currency, and promoting sustainable economic growth.
Monetary policy is broadly categorized into two types:
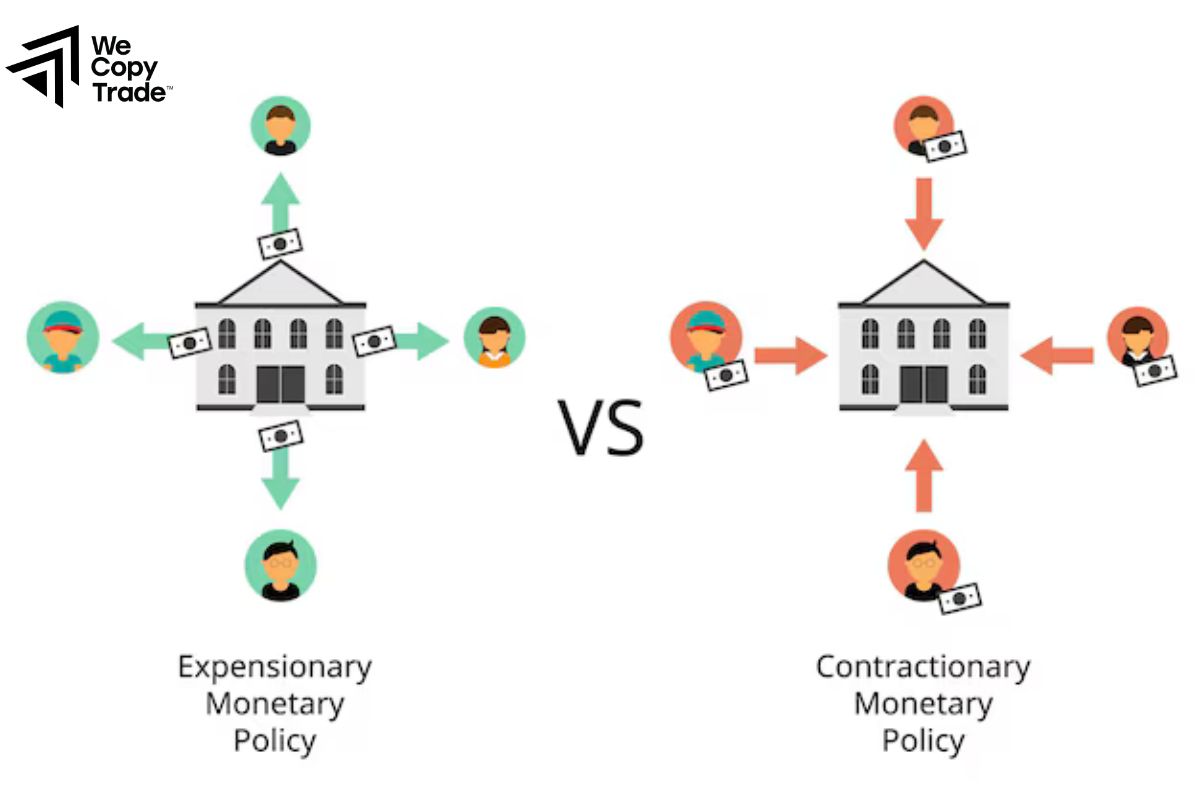
- Expansionary Monetary Policy: Implemented to stimulate economic growth during periods of recession or economic slowdown. This is often achieved by lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply to encourage borrowing and investment.
- Contractionary Monetary Policy: Used to curb inflation when the economy is overheating. Central banks may increase interest rates or reduce the money supply to cool down excessive spending and stabilize prices.
See now:
- Take advantages Industrial Production Index (IPI) In Trading
- How Do Unemployment Rates Impact To Market Vodility?
- Apply The Labor Market Reports Effectively In Forex Trading
Main Objectives of Monetary Policy
The main objectives of Monetary Policy revolve around ensuring a stable and sustainable economic environment. These goals can vary depending on the country’s economic conditions but typically include:
Controlling Inflation

- Maintain price stability by preventing excessive inflation or deflation.
- Ensures that the purchasing power of money remains stable, fostering consumer and business confidence.
Promoting Employment
- Strive for maximum employment by creating favorable conditions for job growth.
- Lower interest rates can encourage businesses to invest and hire more workers.
Economic Growth
- Support steady and sustainable growth by balancing inflation control and employment promotion.
- Encourages investments and consumption for long-term economic health.
Stabilizing Currency Value
- Maintain the stability of the national currency in foreign exchange markets.
- Helps in boosting international trade and investment by reducing currency risks.
Regulating Money Supply

- Ensure adequate liquidity in the economy to meet the needs of businesses and consumers without overheating the market.
- Controls credit availability to avoid financial imbalances.
Managing Interest Rates
- Set benchmark interest rates to influence borrowing and saving behaviors.
- Helps steer the economy toward desired outcomes like increased investment or reduced spending.
Common Types of Monetary Policy
The common types of Monetary Policy are categorized based on their approach to influencing economic conditions. These are primarily:
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Stimulates economic growth during periods of recession or low economic activity.
- Lowering interest rates to make borrowing cheaper.
- Increasing the money supply by purchasing government securities.
- Reducing reserve requirements for banks to encourage lending.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Reduces inflation when the economy is overheating.
- Raising interest rates to make borrowing more expensive.
- Selling government securities to reduce money supply.
- Increasing reserve requirements for banks to limit lending.
Neutral Monetary Policy
Maintains the current economic state without major interventions.
- The central bank keeps interest rates and money supply stable.
Accommodative Monetary Policy
- Supports economic recovery after a downturn by keeping monetary conditions loose.
- Lowering interest rates and increasing liquidity while being more flexible with inflation targets.
- Stimulates growth but risks inflationary pressures if prolonged.
Tools of Monetary Policy
The tools of Monetary Policy are the mechanisms central banks use to influence the economy by controlling the money supply, interest rates, and liquidity. The main tools include:
Open Market Operations (OMO)
Buying and selling government securities in the open market.
- Buying securities injects money into the economy, increasing liquidity.
- Selling securities withdraws money from the economy, reducing liquidity.
Interest Rate Policy

Adjusting the benchmark interest rate, such as the federal funds rate.
- Lowering rates makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging investment and spending.
- Raising rates discourages borrowing, reducing inflationary pressure.
Discount Rate
The interest rate at which commercial banks borrow funds directly from the central bank.
- Lowering the discount rate encourages banks to borrow more and lend more to customers.
- Raising the discount rate reduces borrowing, slowing economic activity.
Quantitative Easing (QE)
A non-traditional tool where the central bank purchases long-term securities to inject money directly into the economy.
- Increases the money supply to stimulate economic activity when traditional tools are insufficient.
- Used during severe recessions or financial crises to boost economic growth.
Inflation Targeting

Setting a specific inflation rate as a policy target (e.g., 2% annually).
- The central bank adjusts its tools (interest rates, OMO, etc.) to maintain inflation within the target range.
- Provides transparency and anchors expectations of businesses and consumers.
Moral Suasion
Persuading financial institutions to act in line with desired its goals through communication rather than mandatory regulations.
- Central banks encourage banks to limit lending or increase liquidity without enforcing strict measures.
- Aligns market behavior with policy objectives in a less intrusive manner.
Comparing Expansionary vs. Tight Monetary Policy
Here is the comparison table between Expansionary Monetary Policy and Tight Monetary Policy:
| Factor | Expansionary Monetary Policy | Tight Monetary Policy |
| Objective | Stimulate growth, reduce unemployment. | Control inflation, stabilize prices. |
| Actions | Lower interest rates, increase money supply. | Raise interest rates, reduce money supply. |
| Impact | Encouraging spending and investment, may lead to inflation. | Slows down spending, reduces investment, controls inflation. |
| Use Case | When the economy is in recession or growing slowly. | When the economy is overheating and inflation is high. |
| Risks | High inflation, asset bubbles. | Slower growth, higher unemployment. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Monetary Policy plays a critical role in managing economic stability by influencing interest rates, money supply, and inflation. Whether through expansionary or tight monetary policies, central banks aim to ensure a balanced and sustainable economy. Understanding how these policies work can help individuals and businesses make informed financial decisions. If you’re looking to stay updated on how policy affects your financial planning, subscribe to our newsletter for expert insights and tips!
See more:
Planning To Measure The PMI For Your Successful Trading
How Do Non-farm Payrolls Impact the Financial Market?
Apply Multiple Time Frames Technology Analysis in Trading
What are emotions in trading? Emotions Traders Experience











