Understanding liquidity risk is crucial for investors and businesses alike. This financial risk arises when an entity struggles to meet its short-term financial obligations due to an inability to quickly convert assets into cash without a significant loss in value. Properly managing can protect your investments and ensure financial stability in volatile markets. Are you prepared to take control of your financial future? Dive deeper into liquidity risk management strategies and empower yourself to make informed decisions today!
What is liquidity risk?

Liquidity risk refers to the potential difficulty an entity faces when trying to convert its assets into cash without significantly affecting the asset’s market price. In other words, it’s the risk that an entity may not be able to meet its short-term financial obligations due to an absence of liquid assets. This type of risk can have serious implications for both individuals and institutions, making it essential to understand and manage effectively.
See now:
- Tips Simplify Your Financial Risks Management Process
- Financial Risk Assessment, Identification and Management
- What is interest rate risk? How to manage interest rates
Liquidity Risk Faced by Investors
Investors encounter liquidity risk when they invest in assets that are not easily tradable or have limited market participation. For example, investing in small-cap stocks, real estate, or private equity can pose liquidity challenges because these assets may take longer to sell or may require significant price concessions to execute a sale quickly.
This risk becomes particularly pertinent during market downturns when the demand for certain assets dwindles. Investors may find themselves unable to sell their holdings quickly, potentially locking in losses or incurring additional costs due to forced selling.
Liquidity Risk Faced by Banks

Banks face liquidity risk primarily through their need to meet withdrawal demands from depositors and other financial obligations. If a bank does not have enough liquid assets, such as cash or easily sellable securities, it may struggle to fulfill these obligations.
In extreme cases, a liquidity crisis can lead to a bank run, where a large number of customers withdraw their deposits simultaneously, fearing the bank’s insolvency. To mitigate this risk, banks must maintain a careful balance between their liquid assets and liabilities, complying with regulatory requirements such as the Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR).
Market Liquidity Risk
Market liquidity risk refers to the risk that an asset cannot be bought or sold quickly enough in the market to prevent a loss. This risk arises from the supply and demand dynamics within the market. In a liquid market, assets can be quickly sold without a significant price reduction. However, in an illiquid market, even a small sale can lead to substantial price drops, exposing investors to higher risks.
Factors influencing market liquidity include economic conditions, market structure, trading volumes, and investor sentiment. Understanding market liquidity risk is crucial for investors to make informed decisions and manage their portfolios effectively.
Incorporating Liquidity Risk
In addressing endogenous liquidity risk, one effective approach is to leverage the depth of the order book to adjust risk metrics. It’s important to note that risk models differ from valuation models, and this method assumes observable order book data.
For instance, consider expected shortfall (ES). Assume a $500,000 investment with a daily volatility of 0.8%. Setting the expected daily return to zero, the 10% one-tailed threshold is 1.28 standard deviations. Thus, the 90% expected shortfall is calculated as:
Expected Shortfall = $500,000 × 0.8% × 1.28 = $5,120
This indicates that on average, we expect daily losses to exceed $5,120 only 10% of the time, not accounting for liquidity.
Assuming the ask price is $15.50 and the bid price is $14.70, the bid-ask spread is:
Spread (%) = (15.50−14.70) / 15.10 ≈ 5.29%
For our liquidity adjustment, we add half the spread. Therefore, the liquidity-adjusted expected shortfall (L-ES) is:
L-ES = $500,000 × [−0+0.8%×1.28+0.5×5.29%] = $13,050.
Thus, the liquidity adjustment increases the expected shortfall by $13,050, reflecting the impact of liquidity costs.
3 steps to successful liquidity risk management
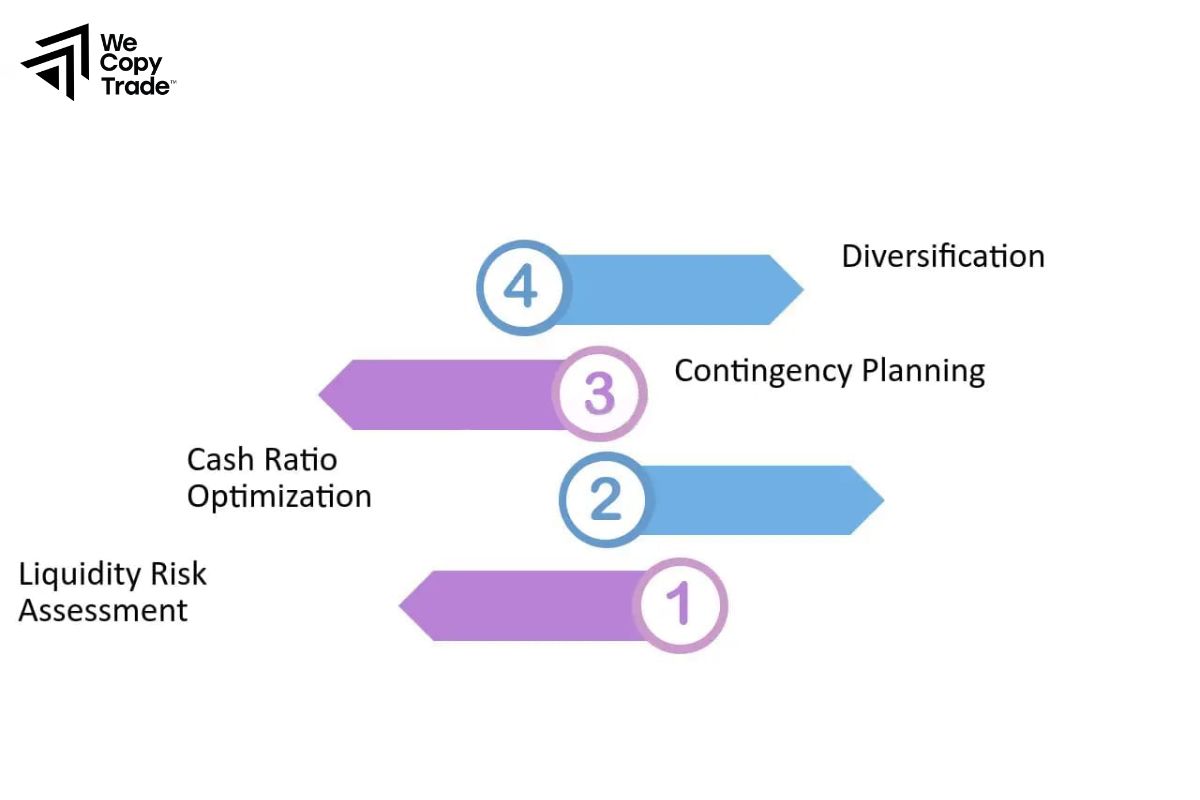
Assessment of Liquidity Needs
Organizations should evaluate their cash flow requirements, considering both expected and unexpected cash outflows. This assessment will help determine the level of liquid assets needed to meet obligations.
Diversification of Liquid Assets
Maintaining a diverse portfolio of liquid assets—such as cash, government securities, and high-quality corporate bonds—can help ensure that funds are readily available when needed.
Regular Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous monitoring of liquidity positions and market conditions is crucial. Establishing a robust reporting framework will help organizations identify potential liquidity risk early and take proactive measures to address them.
Measures of Market Liquidity Risk
Several measures can be used to assess market liquidity, including:
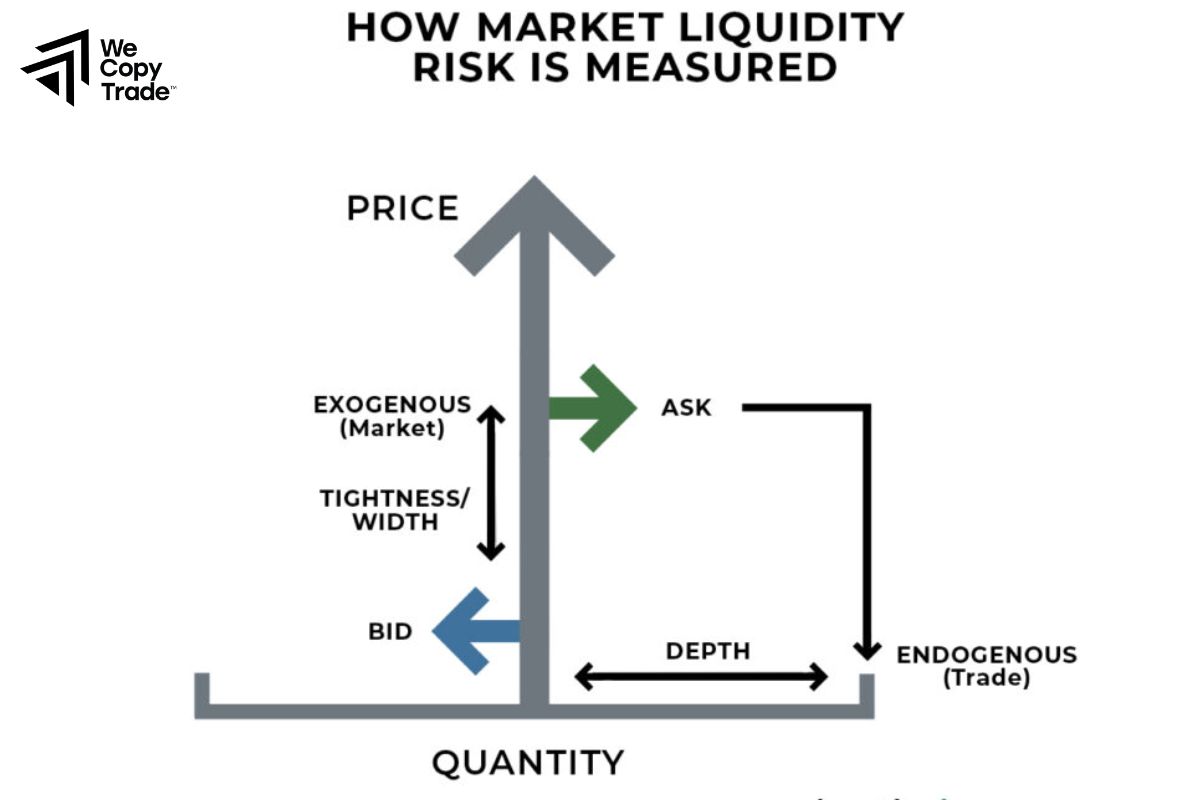
- Bid-Ask Spread: The difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller will accept. A wider spread indicates lower liquidity.
- Trading Volume: Higher trading volumes generally suggest better liquidity, as they indicate active market participation.
- Market Depth: This refers to the market’s ability to absorb large transactions without impacting the price significantly. Deeper markets with more buy and sell orders tend to be more liquid.
- Time to Liquidate: This metric assesses how long it would take to sell an asset without a significant price impact, providing i nsight into its liquidity profile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing liquidity risk is essential for both investors and financial institutions. Don’t leave your investments to chance and take proactive steps to manage liquidity risks today. For more insights and tools on mitigating liquidity risks, explore our resources and empower yourself to make informed financial decisions!
See more:











