Have you ever heard the definition of fiscal policy? It sounds complicated and strange, but if you want to become a successful investor, you must first understand the rules of the market economy. And this policy is the first suggestion for you. Don’t miss the following article, I will turn dry concepts into more interesting and concise. Let’s go!
What Is Fiscal Policy?
Simply put, fiscal policy is how the government uses our tax dollars to influence the economy. When the economy is struggling, the government can spend more or cut taxes to give people more money to spend and invest. Conversely, when the economy is overheating, the government can cut spending or raise taxes to slow it down.
The main goal of this policy is to stabilize the economy, help reduce unemployment, control inflation, and promote economic growth.

For example, a developing country might focus on reducing poverty and improving infrastructure, while a developed country might be concerned with maintaining price stability and protecting the environment.
See now:
Understanding Monetary Policy? Common Types of Policy
Apply The Yield Curve Effectively for Successful Trading
Apply The Labor Market Reports Effectively In Forex Trading
How To Contribute A Good ISM Manufacturing Index In Trading
Who Handles Fiscal Policy?
In the United States, decisions about the country’s finances are made not by one person but by a group of people. The process of deciding on fiscal policy goes like this: The president makes proposals, the Secretary of the Treasury analyzes and evaluates them, and Congress debates and votes. If both the House and Senate agree, a new bill is enacted, becoming the law of the land.
The Impacts of Fiscal Policy on Forex market
Fiscal policy, which includes government tax and spending decisions, plays an important role in shaping a country’s economy. However, the impact of this policy on exchange rates is a complex issue, depending on many different factors and can change over time.
Main factors:
Budget deficit and financing

When a government implements an expansionary fiscal policy, that is, increases spending or reduces taxes, it will lead to a budget deficit. To make up for this deficit, the government often has to borrow or issue bonds.
If the government borrows from abroad, the demand for foreign currency will increase, putting pressure on the exchange rate and possibly causing the domestic currency to depreciate.
Issuing bonds can attract foreign investment, increase the supply of foreign currency and help stabilize or even increase the value of the domestic currency. However, if the bond issuance is too large or unattractive, it can cause inflation and devalue the domestic currency.
Inflation

Expansionary fiscal policy can cause inflation, especially when the economy is near its maximum output. High inflation will reduce the purchasing power of the domestic currency and put pressure on the exchange rate.
Investor Expectations
Investors’ expectations about future economic policies also have a big impact on the exchange rate. If investors expect interest rates to rise or inflation to increase, they may sell the domestic currency and buy foreign currency, putting pressure on the exchange rate.
Components of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy is a tool that the government uses to regulate the economy through the management of revenue and expenditure. The three main pillars of this policy include:
- Public spending: is the government’s spending to provide public services and invest in development projects. Specifically, the government will spend money on areas such as infrastructure construction, education, health, defense, etc. Increasing public spending can create more jobs, stimulate consumption and investment, thereby promoting economic growth.

- Taxes: This is the government’s main source of revenue, collected from individuals and organizations to finance spending activities. Adjusting tax rates can affect the motivation of people and businesses to work, consume and invest.
- Debt: When government spending exceeds tax revenue, the government can borrow to balance the budget. However, borrowing too much can put pressure on national finances and increase the debt burden for future generations.
Types of Fiscal Policies
A country’s fiscal policy is like managing a family’s budget. There are three main approaches:
Neutral
“Neutral fiscal policy” means that the government spends exactly what it collects in taxes. This balanced budget helps maintain economic stability, preventing excessive inflation or recession.
Expansionary
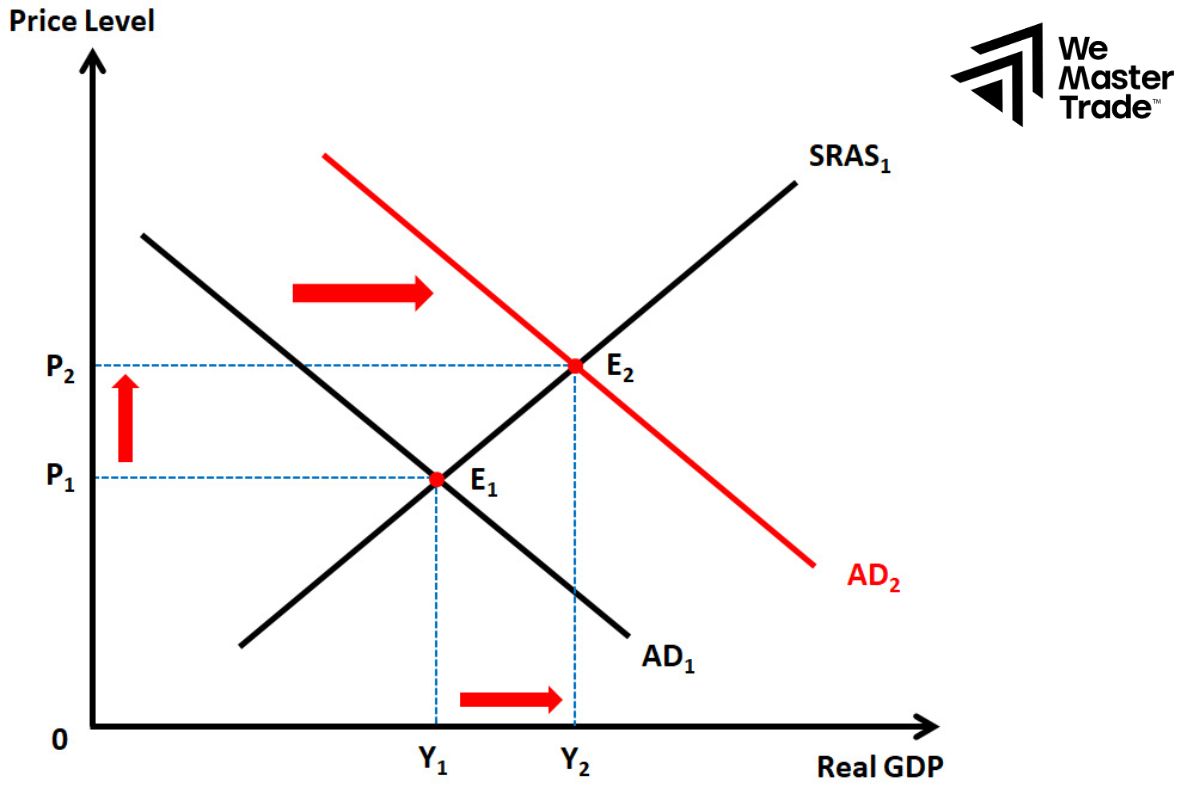
To revive an economy when it is in trouble, governments often use fiscal tools such as cutting taxes or increasing public spending.
For example, by cutting personal income taxes, people will have more money to spend, thereby stimulating production and creating jobs. Or, the government can invest in public projects such as building roads and bridges to create jobs and boost economic growth. However, increasing public spending often leads to a budget deficit, meaning the government has to borrow money to cover the difference between revenue and expenditure. However, in times of economic hardship, budget deficits are often seen as a necessary measure to stabilize the economy.
Tightening
To curb inflation and stabilize an overheated economy, governments can implement a contractionary fiscal policy. This involves raising taxes, cutting government spending, and even cutting public sector jobs. The goal of this policy is to reduce the amount of money supplied to the economy, thereby reducing purchasing power and putting upward pressure on prices. However, a contractionary fiscal policy often has negative short-term consequences, such as slowing economic growth and increasing unemployment. Therefore, governments often consider this policy very carefully before adopting it and often prioritize using other tools such as monetary policy to adjust the economy.
Fiscal Policy vs. Monetary Policy
Fiscal policy and monetary policy are the two main tools that governments use to manage the economy, each with its own characteristics and impacts.
- Fiscal policy is directly related to the state’s revenue and expenditure. When the government increases public spending (for example, investing in infrastructure construction, increasing salaries for officials and employees) or reduces taxes, the economy will be stimulated. Conversely, when spending is reduced or taxes are increased, the economy will be slowed down.
- Monetary policy focuses on adjusting the amount of money supply in the economy, usually done by the central bank. By changing the base interest rate, buying and selling government bonds or adjusting the reserve requirement ratio, the central bank can affect the cost of borrowing, thereby affecting investment and consumption of households and businesses.
Although different in their tools, both policies aim at the common goal of stabilizing the economy, controlling inflation and ensuring full employment. However, the effectiveness of each policy will depend on many factors, including the specific economic situation of each country.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fiscal policy is considered one of the leading economic solutions. Moreover, the relationship between this policy and exchange rate is very complex and cannot be simplified. To make an accurate forecast of the impact of fiscal policy on exchange rate, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the economic, political and social factors at play. Good luck
See more:
The Importance of Interest Rate Forecasting In Trading
What is the Trade Balance? How to Calculate Balance Trading
How Do Unemployment Rates Impact To Market Vodility?











