Have you ever heard of the term bond spreads? To limit risks in the investment and trading process, you must learn carefully about this difference. Don’t hesitate to take a few minutes to follow the following article with all the information you need! Let’s go!
What is Bond Spreads?
A bond spread is the difference between the yield of a particular bond and that of a benchmark bond (usually a government bond). This spread shows how much more risk an investor is willing to accept to own that bond.
The price of a currency when compared to another currency is known as the exchange rate. As the bond spread increases, the currency of the country with the higher yield tends to appreciate relative to the currency of the country with the lower yield.
See now:
- Understand The Importance Of Fiscal Policy In Trading Market
- Planning To Measure The PMI For Your Successful Trading
- Why is National Debt Important? The Structure of National
- The Importance of Interest Rate Forecasting In Trading
What does Bond spreads tell you?
A high spread indicates that the bond is riskier. Conversely, a low spread indicates that the bond is safer.
When the spread is too large compared to normal, there may be an attractive investment opportunity. For example, if a corporate bond is of good quality but has a high spread, it means that it is undervalued.
By investing in bonds with different spreads, you can diversify your risk and increase the return potential of your portfolio.
The general spread of the bond market can reflect the general economic situation. When the economy is stable, the spread is usually low. Conversely, when the economy is struggling, the spread is often high.

Suppose there are two bonds:
- Bond A: Issued by an emerging technology company that has high growth potential but also has bankruptcy risk.
- Bond B: Issued by a large, stable power company with low growth potential. Bond A will typically have a higher spread than bond B because of the higher risk. However, if the spread on bond A is too large compared to normal, it may indicate that it is undervalued and has high potential for growth.
The Relationship Between Currencies and Bond Spreads between 2 different Countries
Investors always want to find a place to put their money to get the highest return. When a country has a higher interest rate, investors will put money in it, pushing the value of that country’s currency up.
Professional investors will take advantage of the interest rate differential to make a profit. They will borrow money in a country with a low interest rate and invest in a country with a high interest rate. This also contributes to pushing up the value of the currency of the country with a high interest rate.
What is the interest rate differential?

The interest rate differential is the difference between the interest rates of two countries. When a country has a higher interest rate, investors will put money in that country to earn a higher return, pushing up the value of that country’s currency.
Interest rates are a key instrument employed by central banks to manage economic activity. When they want to stimulate the economy, the central bank will reduce interest rates to encourage investment and consumption. Conversely, when they want to curb inflation, central banks will raise interest rates to reduce demand.
For example, after the 2008 financial crisis, many countries cut interest rates to near zero to stimulate their economies. This created a large gap between interest rates in developed and developing countries. Investors sought out emerging markets with higher interest rates to invest in, pushing up the value of their currencies.
The Relationship Between Interest Rates, Currencies and Bond Spreads between 2 Different Countries
Investors are always looking for higher returns. When interest rates in a country rise, capital flows into that country, pushing up the value of its currency. When the interest rate differential between two countries increases, the currency of the country with the higher interest rate tends to appreciate relative to the currency of the country with the lower interest rate.

For example, when the interest rate differential between Australia and the US increases, the Australian dollar tends to appreciate relative to the US dollar.
By monitoring interest rate differentials, investors can predict the trend of exchange rate movements in the near future and build effective forex trading strategies.
The Impact of Yield Spreads on Bond Spreads
The spread between bond yields not only reflects current interest rates but is also an important indicator of market expectations for future monetary policy. Changes in these expectations can have a strong impact on exchange rates before monetary policy actually changes.
What is a yield spread?
It is the difference between the yields of bonds with different maturities. For example, the difference between the yields of 5-year and 10-year bonds can show investors’ expectations for future interest rates.
The role of central banks
The central bank’s decision to raise or lower interest rates will directly affect the yield spread and thus affect the exchange rate.
Even if the central bank has not officially made a decision, if the market expects the central bank to change policy, the exchange rate will also react in advance.

For example: The Federal Reserve (Fed): When the Fed signals that it wants to tighten monetary policy, the US dollar often appreciates, even before actual interest rates rise. This shows that the market has already reacted to expectations of a rate hike.
Yield Spreads on Bond Spreads Relationships
The yield spread shows how investors assess the risk of a bond. A bond with higher risk (e.g., a company that is more likely to go bankrupt or not pay interest) will be priced lower. To attract investors, this bond will have to pay a higher interest rate. A safer bond (e.g., a government bond) will be priced higher. Because investors feel more secure, they accept a lower interest rate.
The yield spread helps investors compare the value of bond spreads. Bonds with higher yields are typically priced lower than bonds with lower yields.
For example:
- Bond A: Yield 3%.
- Bond B: Yield 1%.
- Spread: 2% (or 200 basis points).
This means:
- Investors perceive bond A as riskier than bond B, so they demand a higher yield to compensate for this risk.
- Because of the higher risk, the price of bond A may be lower than that of bond B.
How to Use the Yield Curve to Trade Bonds
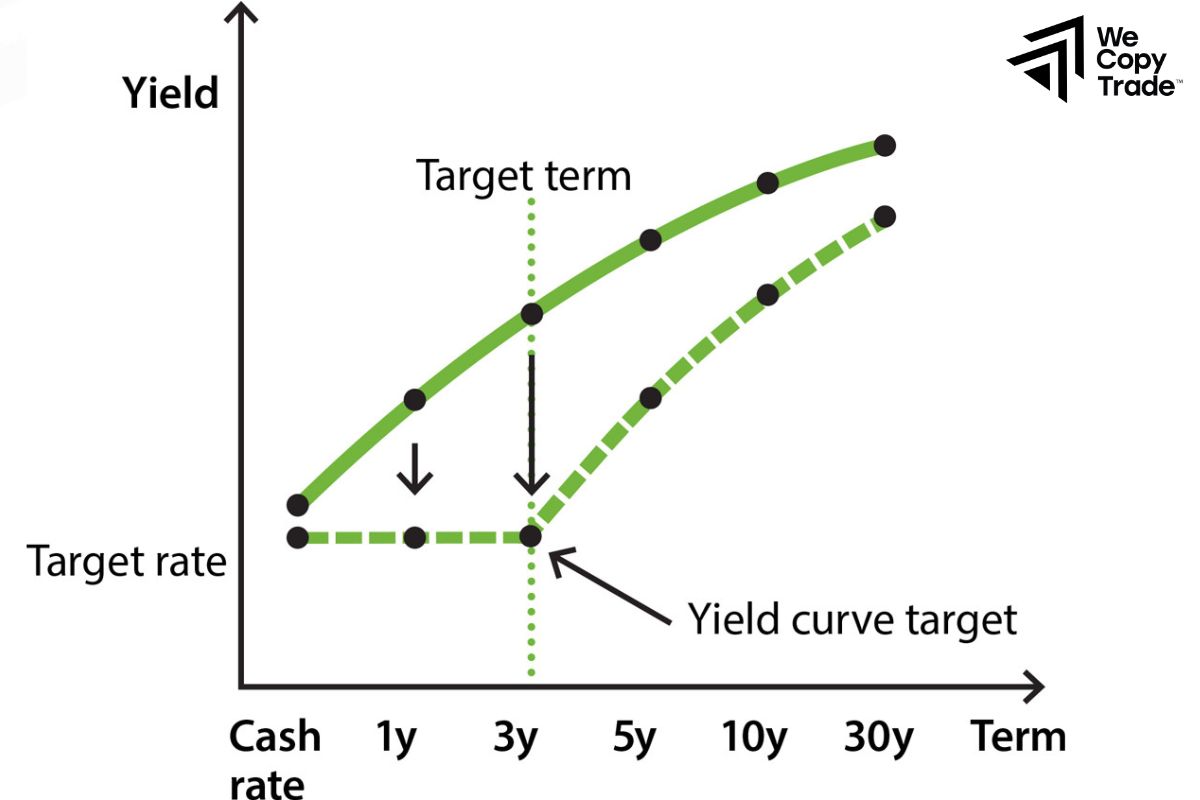
When investors are fearful, they sell long-term bonds (in fear of rising interest rates) and buy short-term bonds. This causes the yield curve to invert (short-term bond yields are higher than long-term bond yields). This is often a sign of a recession.
When investors are optimistic, they buy long-term bonds in search of higher returns. This causes the yield curve to slope upward (long-term bond yields are higher than short-term bond yields). This is often a sign of a recovering economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bond spreads are one of the important factors that help investors assess risks, find opportunities and diversify their investment portfolio. You can predict the trend of a currency pair and make better investment decisions based on bond spread. Good luck!
See more:











