Contractionary Policy is a crucial economic tool used by governments and central banks to control inflation and stabilize the economy. By reducing the money supply or increasing interest rates, contractionary fiscal and monetary policies aim to slow down an overheating economy. Curious about how contractionary policies could impact your investments or business? Keep reading to discover key insights and strategies to stay ahead!
What is a Contractionary Policy?

A Contractionary Policy is an economic strategy used by governments or central banks to reduce the overall level of economic activity, typically with the goal of controlling inflation or stabilizing an overheated economy. This can be implemented through two main types of policies:
- Contractionary Monetary Policy: This involves actions by a central bank, such as increasing interest rates or reducing the money supply. By raising interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive, which reduces consumer spending and business investment, thereby cooling down inflationary pressures.
- Contractionary Fiscal Policy: This involves the government reducing its spending or increasing taxes to decrease the overall demand in the economy. Lower government spending and higher taxes can reduce disposable income and decrease consumption, helping to slow inflation.
See now:
- What is the Trade Balance? How to Calculate Balance Trading
- The PPI: definition, relationship with Inflation, strategy
- Apply The Labor Market Reports Effectively In Forex Trading
- How To Avoid Common Mistakes In Trading Psychology
Tools Used for Contractionary Policies
Contractionary policies are designed to reduce economic activity, typically to combat inflation or an overheating economy. The main tools used for contractionary policies include:
Monetary Policy Tools
- Raising Interest Rates: Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, can increase the federal funds rate (or other key interest rates) to make borrowing more expensive. This tends to reduce consumer spending and business investment, thereby slowing down economic activity.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs): The central bank may sell government securities to reduce the amount of money circulating in the economy, which increases interest rates and decreases lending.
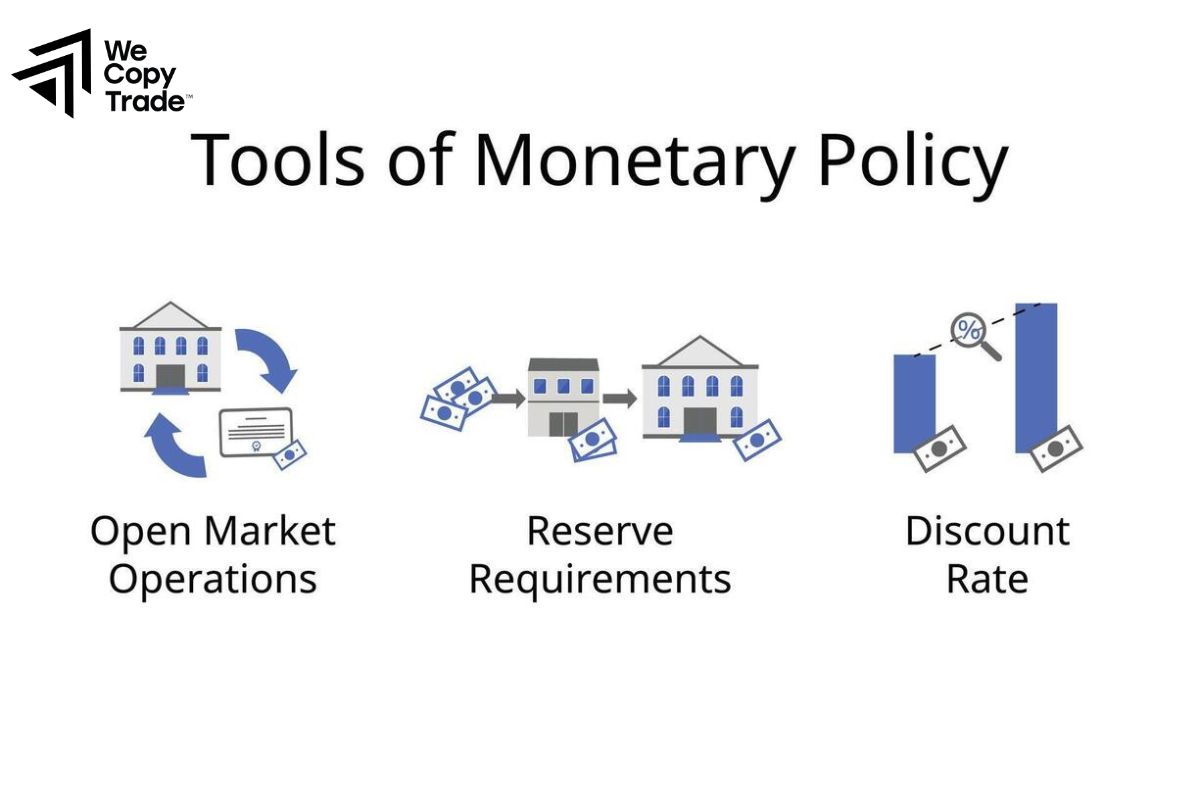
- Increasing Reserve Requirements: By raising the reserve requirement (the percentage of deposits banks must hold in reserve), the central bank limits the amount of money banks can lend out, reducing the money supply.
- Discount Rate: The central bank may increase the discount rate, which is the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow from the central bank. Higher rates discourage borrowing and reduce the money supply.
Fiscal Policy Tools
- Reducing Government Spending: The government can cut back on public spending, especially on social welfare programs, infrastructure, and other public investments, which reduces aggregate demand in the economy.
- Increasing Taxes: Higher taxes reduce disposable income for consumers and businesses, thereby decreasing consumption and investment.
Currency Appreciation
- A stronger currency can help reduce inflation by making imports cheaper, which can lower domestic prices and demand.
What Are the Effects of Contractionary Policy?

Contractionary Policy typically have the following common effects:
- Reduced Inflation: Contractionary policies help control inflation by reducing the money supply and demand in the economy, which slows down the rate of price increases.
- Slower Economic Growth: Increasing interest rates and cutting government spending result in lower consumer spending and business investment, which slows down the overall economic growth rate.
- Higher Unemployment: Businesses may reduce production and lay off workers when demand decreases, leading to higher unemployment rates.
- Reduced Consumer Spending and Investment: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumers’ ability to spend and businesses’ willingness to invest.
- Stronger Currency: Contractionary monetary policy, especially through higher interest rates, can strengthen the national currency, making exports more expensive and imports cheaper.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Contractionary Policy
Advantages of Contractionary Policy

- Control Inflation: The primary advantage of contractionary policies is their ability to reduce inflation.
- Maintain Economic Stability: Contractionary policies can help maintain long-term economic stability by avoiding excessive growth and the formation of economic bubbles, particularly in asset markets like real estate or stocks.
- Strengthen the Currency: When interest rates rise, foreign investors may be attracted by higher returns, leading to a stronger national currency. This can make imports cheaper and help reduce trade deficits.
- Build Confidence in the Economy: Controlling inflation and stabilizing the economy can help build confidence among consumers and investors, providing a foundation for sustained, balanced growth in the future.
Disadvantages of Contractionary Policy:

- Risk of Recession: If contractionary policies are too aggressive or maintained for too long, they can trigger a recession. A prolonged period of reduced demand can result in negative growth, causing widespread economic hardship.
- Negative Impact on Debt-Ridden Sectors: For businesses or governments that rely heavily on borrowing, higher interest rates increase the cost of servicing debt. This can lead to financial strain, particularly for highly leveraged entities.
- Stronger Currency Can Hurt Exports: While a stronger currency might lower import costs, it can also make exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially hurting industries reliant on international trade.
Contractionary Policy vs. Expansionary Policy
| Factor | Contractionary Policy | Expansionary Policy |
| Purpose | Reduce inflation and control excessive economic growth. | Stimulate economic growth and reduce unemployment. |
| Tools Used | Increase interest rates, sell bonds, reduce government spending, increase taxes. | Lower interest rates, buy bonds, increase government spending, lower taxes. |
| When to Use | When the economy is growing too fast, inflation is high. | When the economy is in a recession, unemployment is high. |
| Example | Increase taxes, central bank raises interest rates. | Cut taxes, central bank lowers interest rates. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Contractionary Policy plays a crucial role in stabilizing an economy by controlling inflation and preventing excessive economic growth. By utilizing tools such as increased interest rates, reduced government spending, and higher taxes, policymakers can effectively manage economic overheating. Visit our website for more detailed articles and expert analyses on economic policies!
See more:











