Understand Position Sizing to optimize your trading strategy! Use effective position sizing techniques to manage risk, maximize profits, and maintain balance in your portfolio. Discover the article below to learn how to apply position sizing today and elevate your trading!
What is Position Sizing?
Position sizing is a risk management strategy in trading and investing that determines the amount of capital to allocate to a particular trade or investment. It helps traders control how much they risk on each trade relative to their total portfolio, allowing them to balance risk and reward effectively.

Key points to understand about position sizing:
- Risk Control: Position sizing is essential for managing risk. By adjusting the size of a position based on factors like risk tolerance and the volatility of the asset, traders can ensure they don’t expose too much of their capital to a single trade.
- Portfolio Protection: It helps protect the overall portfolio by limiting losses from any one trade. For example, a trader might choose to risk only 1-2% of their portfolio per trade to avoid large losses.
- Reward Optimization: When used correctly, position sizing allows traders to maximize potential returns while controlling losses, as it helps in scaling positions according to the perceived risk and reward of a trade.
- Various Approaches: There are different methods to calculate position size, such as fixed fractional sizing, volatility-based sizing, and Kelly Criterion.
See more:
- Martingale or Anti-Martingale Strategy? Which one is better?
- Definition, Pros and Cons of Using Martingale Strategy
- Methods To Calculate and Minimize The Fixed Risk per Trade
What are the popular Position Sizing methods?
Here are some popular position sizing methods that traders and investors often use to manage risk and optimize returns:
Fixed Dollar Position Sizing
- Allocate a fixed dollar amount to each trade regardless of portfolio size or market conditions.
- Simple to implement, easy for beginners.
- Does not adjust for the risk level or portfolio changes, which may limit risk control.
Fixed Fractional Position Sizing
- Allocate a fixed percentage of the portfolio for each trade (e.g., 1-2% of the total portfolio).
- Helps to manage risk consistently, preventing overexposure on any single trade.
- Can lead to smaller positions in volatile markets if the percentage is conservative.
Volatility-Based Position Sizing
- Adjust position size based on the asset’s volatility, typically measured by indicators like the Average True Range (ATR).
- Adapts to changing market conditions, reducing position sizes in volatile markets to limit risk.
- More complex and may require additional calculations or tools.
Kelly Criterion
- Calculates position size based on an optimal percentage derived from the expected return and the win/loss probability of the trade.
- Maximizes growth potential based on statistical probabilities.
- Complex and requires precise information about trade probabilities, which can be hard to estimate accurately.
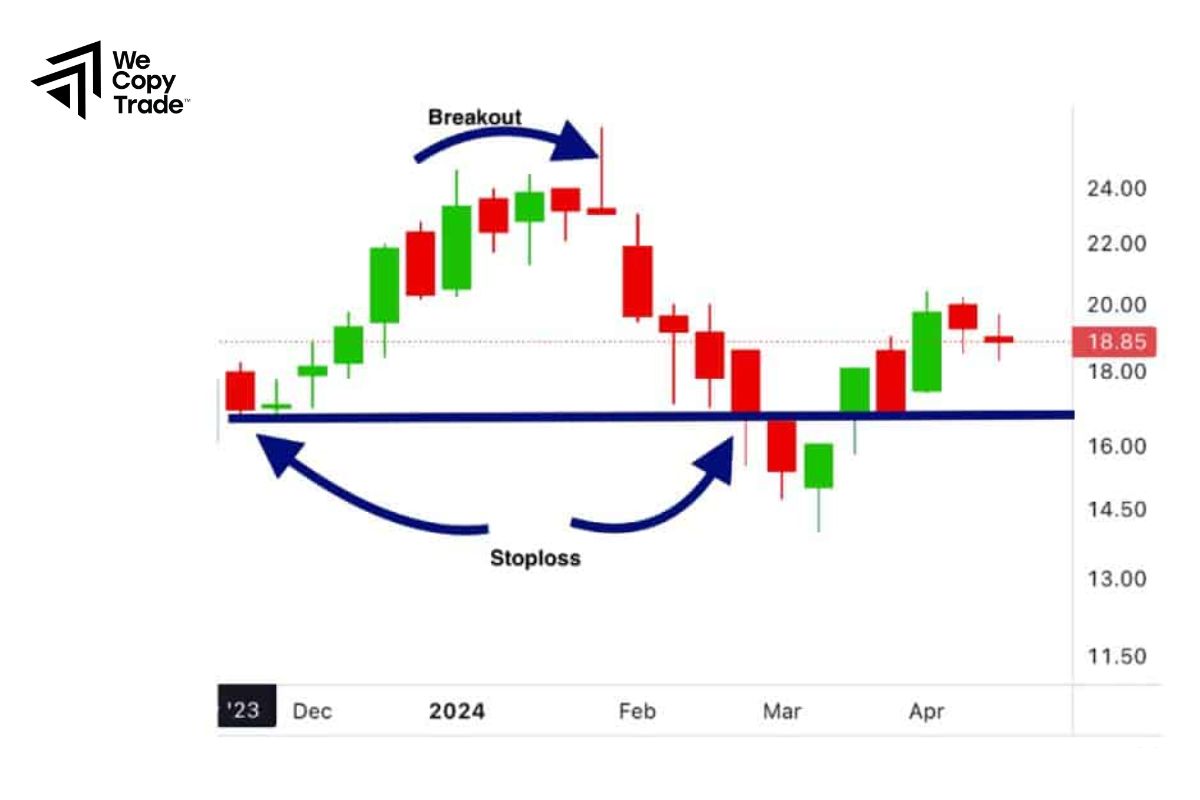
Martingale and Anti-Martingale
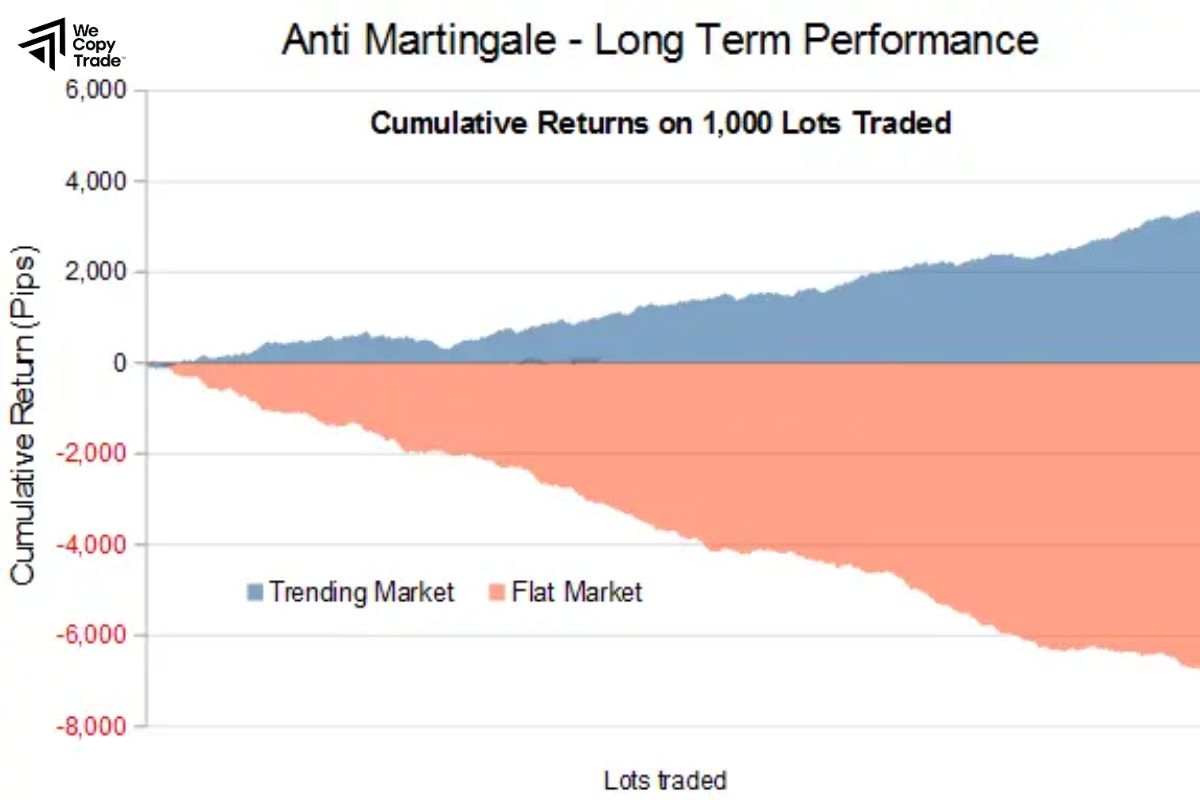
- Martingale: Double the position size after each loss, aiming to recover losses with one winning trade.
- Anti-Martingale: Increase position size after wins and decrease after losses.
- Can be profitable if used carefully with Anti-Martingale in trending markets.
- Martingale is extremely high-risk and can lead to large losses; Anti-Martingale can underperform in volatile markets.
Percentage of Volatility (Risk Parity)
- Balances risk by allocating capital based on each asset’s volatility, so each position has similar risk exposure.
- Helps maintain balanced risk across diverse assets.
- Can lead to smaller positions in volatile assets, potentially limiting profits.
How do you calculate your position size?
Calculating position size is essential for managing risk and maximizing returns. Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating your position size:
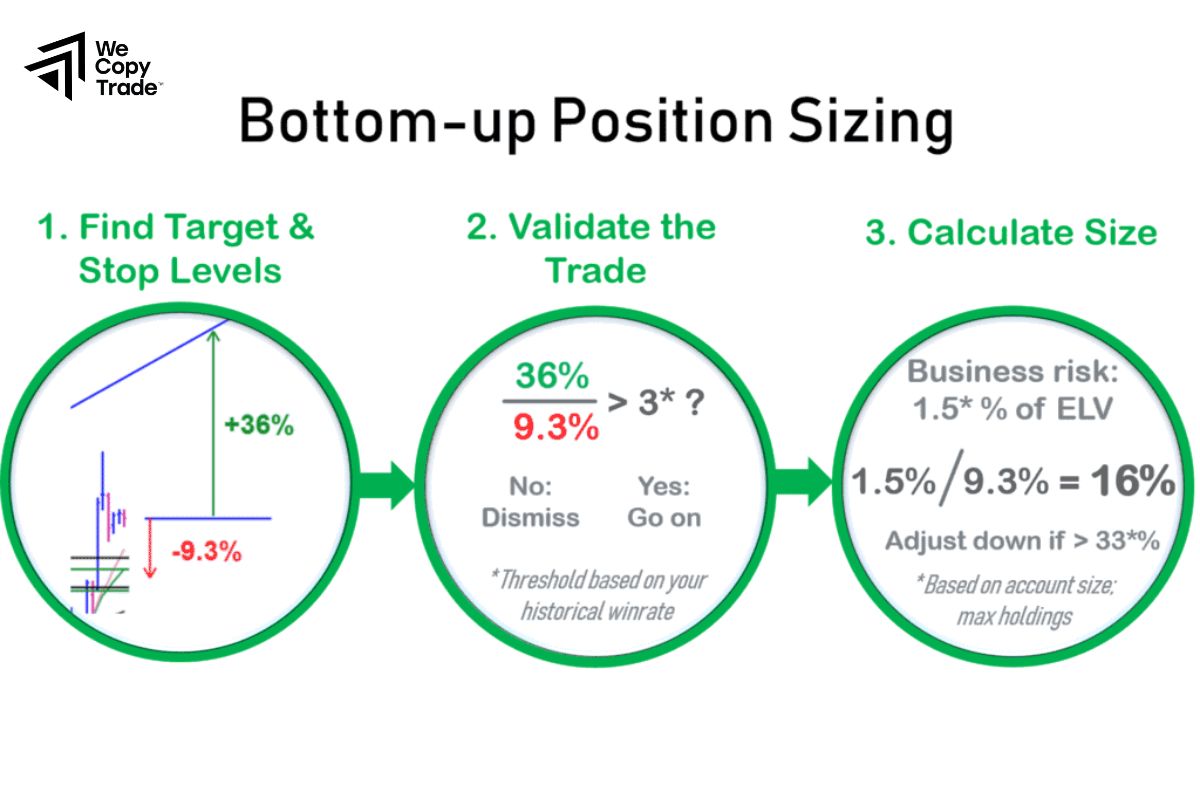
Determine Your Account Risk Tolerance
- Decide how much of your total portfolio you’re willing to risk on a single trade, typically 1-2% for most traders.
- For example, if you have a $10,000 account and you’re willing to risk 2%, your risk tolerance per trade is $200.
Define Trade Risk (Stop-Loss Distance)
- Calculate the difference between your entry price and stop-loss price for the trade.
- For instance, if you’re buying a stock at $100 and setting a stop-loss at $95, your trade risk is $5 per share.
Calculate Position Size
- Use this formula to determine position size:
Position Size = Account Risk / Trade Risk
- In the example above, with a $200 account risk and $5 trade risk:
Position Size = 200 / 5 = 40 shares
This calculation means you would buy 40 shares to keep your risk within $200.
What factors can affect Position Sizing?
Position sizing is influenced by several key factors:
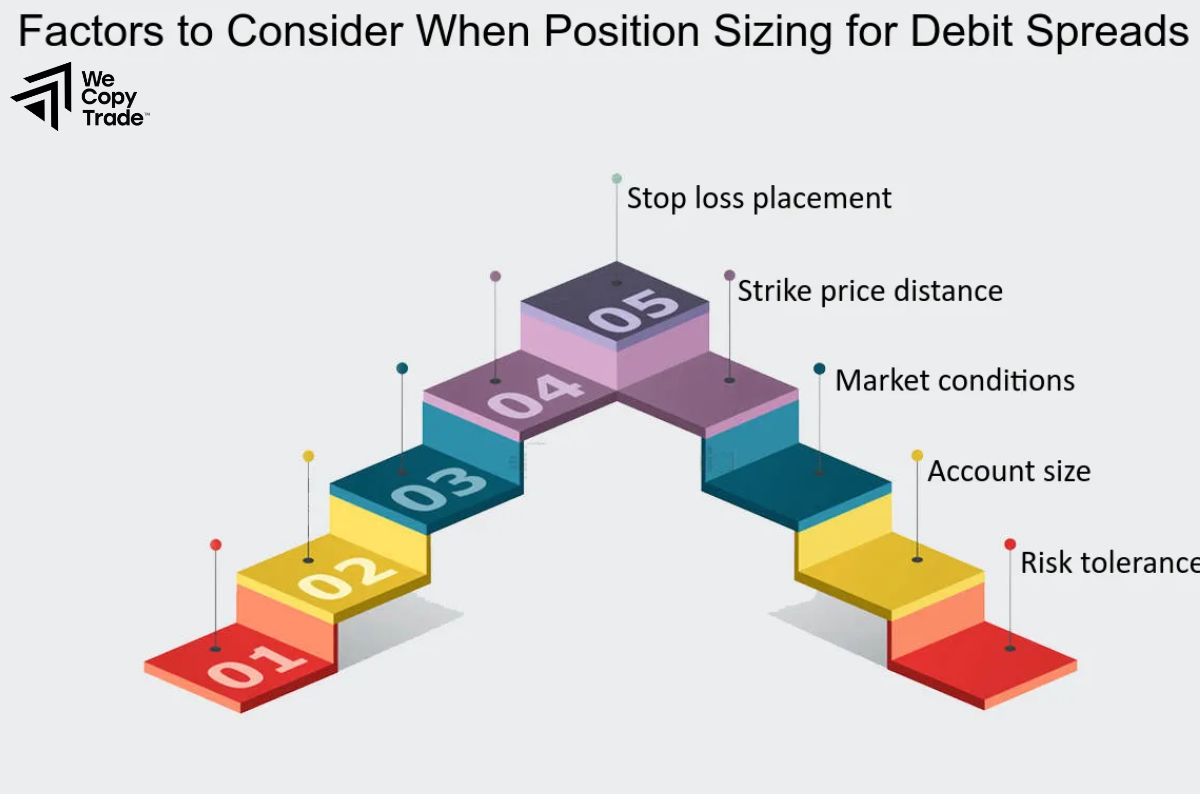
- Account Size: Larger accounts may take on slightly larger positions; smaller accounts require more conservative sizing.
- Risk Tolerance: Determines how much of your capital you’re comfortable risking per trade (usually 1-3%).
- Market Volatility: High volatility demands smaller positions, while lower volatility allows larger ones.
- Stop-Loss Distance: The distance from entry to stop-loss affects position size; wider stops mean smaller positions.
- Strategy and Time Horizon: Short-term strategies may use larger positions with tight stops; long-term investors usually use smaller positions.
- Asset Correlation: Highly correlated assets can compound risk, so adjust position sizes accordingly.
- Leverage: Leverage allows larger positions but increases risk, so use carefully.
What are the benefits of using Position Sizing?
Using position sizing offers several key benefits in trading and investing:
- Controls the amount of capital at risk in each trade, helping to protect the overall portfolio from large losses.
- Maintains a disciplined approach to risk, allowing traders to apply the same strategy across different trades, regardless of emotional or market shifts.
- Optimizes returns by adjusting position sizes based on risk-reward ratios, allowing for larger gains on high-probability trades.
- Adapts to market conditions by adjusting position sizes in volatile markets, helping to avoid overexposure.
- Encourages objective decision-making by basing trade size on calculated risk rather than impulses, leading to better long-term results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering position sizing is essential for effective risk management and long-term trading success. By carefully adjusting your trade size, you can protect your capital, enhance profits, and make smarter trading decisions. Ready to take control of your portfolio? Start applying position sizing techniques today and watch your trading strategy improve!
See now:











