Welcome to Trade Wars, the ultimate strategy game where you compete to build powerful empires, trade resources, and outsmart your rivals. In this fast-paced game, every decision counts—will you dominate the market or fall behind? Whether you’re a seasoned strategist or a newcomer, Trade War offers endless challenges and rewards. Ready to take control and conquer the trade world? Start playing now and prove your skills in the global marketplace!
What are Trade Wars?

Trade wars are economic conflicts between countries where parties impose measures such as tariffs and import restrictions to protect their economy and exert pressure on their opponents. The goal is usually to change economic policies or gain control over international markets.
Trade wars have existed for a long time, from conflicts in ancient times such as between Greece and Rome to 19th-century struggles when industrialized nations protected their economies. A notable example is the tariff war between Britain and France in the early 19th century. In the 21st century, the trade war between the U.S. and China (starting in 2018) became a significant event when the U.S. imposed high tariffs on Chinese goods, leading to retaliatory measures and having a major impact on the global economy.
See now:
- Distinguish Debt vs. Deficit To Make Best Trading Decision
- Hidden Truths About Bond Spreads Not Everyone Knows
- Why is National Debt Important? The Structure of National
Factors Driving Trade Wars
Several factors can drive countries into trade wars, where economic conflicts arise over trade policies and practices. These factors include:
Trade Imbalances
One of the most common causes of trade wars is a significant trade imbalance, where one country imports far more than it exports. Countries with trade deficits may impose tariffs to reduce imports and protect domestic industries.
Unfair Trade Practices
Accusations of unfair trade practices, such as dumping (selling products at unfairly low prices to undercut competitors) or subsidies for domestic industries, can lead to trade wars. Countries may retaliate with tariffs or restrictions to level the playing field.
Protectionism
Governments may adopt protectionist policies to shield their domestic industries from foreign competition. By raising tariffs or imposing other barriers to trade, countries aim to support local businesses and protect jobs.
Economic and Political Rivalries
Trade wars can also be fueled by political or strategic competition. Nations may engage in economic conflicts to exert influence, retaliate against rival governments, or weaken political adversaries.
Intellectual Property (IP) Disputes

Disputes over intellectual property rights, such as patent theft or forced technology transfers, can trigger trade wars. Countries with significant IP concerns may impose tariffs or sanctions to protect their innovations.
National Security Concerns
Countries may initiate trade wars under the guise of national security concerns, especially when foreign goods or investments are perceived as threats to key industries, infrastructure, or technological capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Trade War
Advantages of a Trade War
- Tariffs and trade barriers can shield domestic businesses from foreign competition, giving them time to grow and become competitive.
- Helps preserve jobs in key industries by reducing reliance on imports.
- Imposing tariffs can reduce trade deficits by discouraging imports and encouraging domestic production.
- Promotes the purchase of locally made goods, boosting the national economy.
- Reduces dependence on foreign goods, prompting countries to invest in self-sufficiency.
- Encourages innovation and diversification in domestic industries.

Disadvantages of a Trade War
- Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers.
- Trade wars disrupt global supply chains, leading to inefficiencies, production delays, and economic uncertainty.
- Retaliatory measures can harm export-driven industries and overall economic growth.
- Escalating trade war creates volatility in financial markets, affecting investments and global trade relations.
- Can weaken international cooperation and damage diplomatic relationships.
- Retaliatory tariffs can hurt domestic exporters, leading to reduced demand for their goods and job cuts.
- Companies reliant on international supply chains may struggle with increased costs.
- Developing nations are often disproportionately affected, as they rely heavily on exports for economic growth.

Example of a Trade Wars
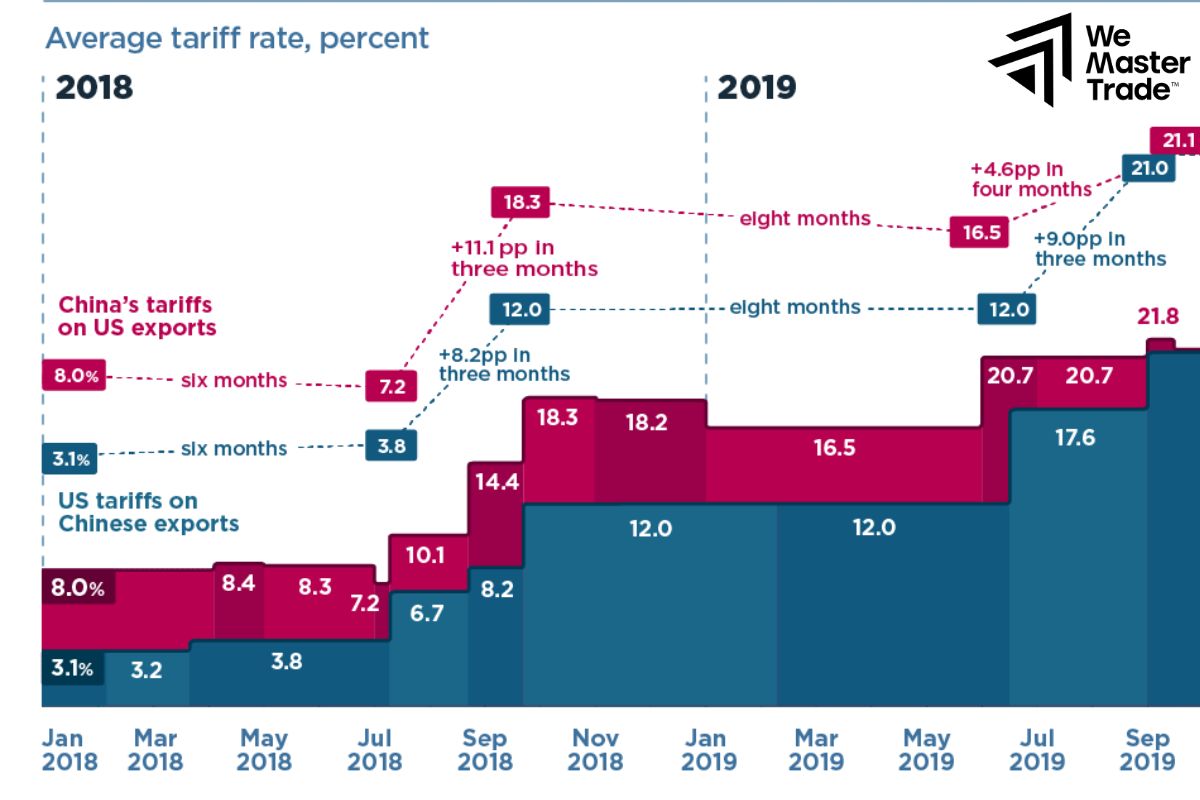
The U.S.-China Trade War began in 2018, primarily due to U.S. concerns over trade imbalances, intellectual property theft, and unfair trade practices by China. The U.S. imposed tariffs on $34 billion worth of Chinese goods, which led to China retaliating with tariffs on U.S. exports, including soybeans and pork.
Over the next two years, both countries escalated tariffs, affecting global supply chains, raising costs for consumers, and slowing economic growth. In January 2020, a Phase One agreement was reached, with China agreeing to buy $200 billion of U.S. goods in exchange for tariff reductions.
Impacts:
- U.S. farmers were hurt by China halting imports of key agricultural products.
- Global supply chains faced disruptions, particularly in tech industries.
- Both economies slowed, and financial markets became volatile.
- The trade war fueled the U.S.-China rivalry and global economic uncertainty.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can trade wars lead to a recession?
Yes, prolonged trade war can contribute to economic slowdowns or even a recession. They can reduce global demand, increase costs for businesses, and disrupt investment patterns, leading to a decline in overall economic activity.
Who benefits from a trade war?
While the ultimate goal of a trade war is often to protect domestic industries, the real beneficiaries are usually specific sectors that are shielded from foreign competition, such as local manufacturers or industries vital to national security.
How do trade wars impact global economies?
Trade wars disrupt global supply chains, reduce trade flows, and cause market instability. Countries involved may face slower economic growth, job losses, and reduced foreign investment. The global economy often suffers due to uncertainty and declining international cooperation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Trade wars can disrupt global markets, raise consumer prices, and strain international relations. While they may offer short-term protection for domestic industries, the long-term effects often include economic challenges for businesses and consumers alike. Stay informed about the implications of trade war to better navigate these global shifts. Explore more on how trade war affects you and your business stay ahead with expert insights and analysis.
See more:











