Understanding Foreign Currency Effects is essential for businesses and investors operating in global markets. Currency fluctuations can significantly impact profits, trade balances, and investment returns. Learn how to identify these effects, implement strategies to mitigate risks, and turn challenges into opportunities. Dive into expert insights and actionable tips today to safeguard your financial success don’t wait, start now!
What Are Foreign Currency Effects?

Foreign Currency Effects refer to the impact of currency exchange rate fluctuations on international transactions, financial statements, investments, and business operations. These effects occur when the value of one currency changes relative to another, influencing the cost of imports and exports, the valuation of overseas investments, and the profitability of multinational corporations.
For businesses, foreign currency effects can lead to gains or losses depending on how exchange rates move. Investors may also experience changes in the value of their international assets due to currency appreciation or depreciation. Understanding and managing these effects is crucial for minimizing risks and maximizing returns in a global economy.
See now:
- Understanding Monetary Policy? Common Types of Policy
- Understand The Importance Of Fiscal Policy In Trading Market
- How To Contribute A Good ISM Manufacturing Index In Trading
Key Factors Influencing Foreign Currency Effects
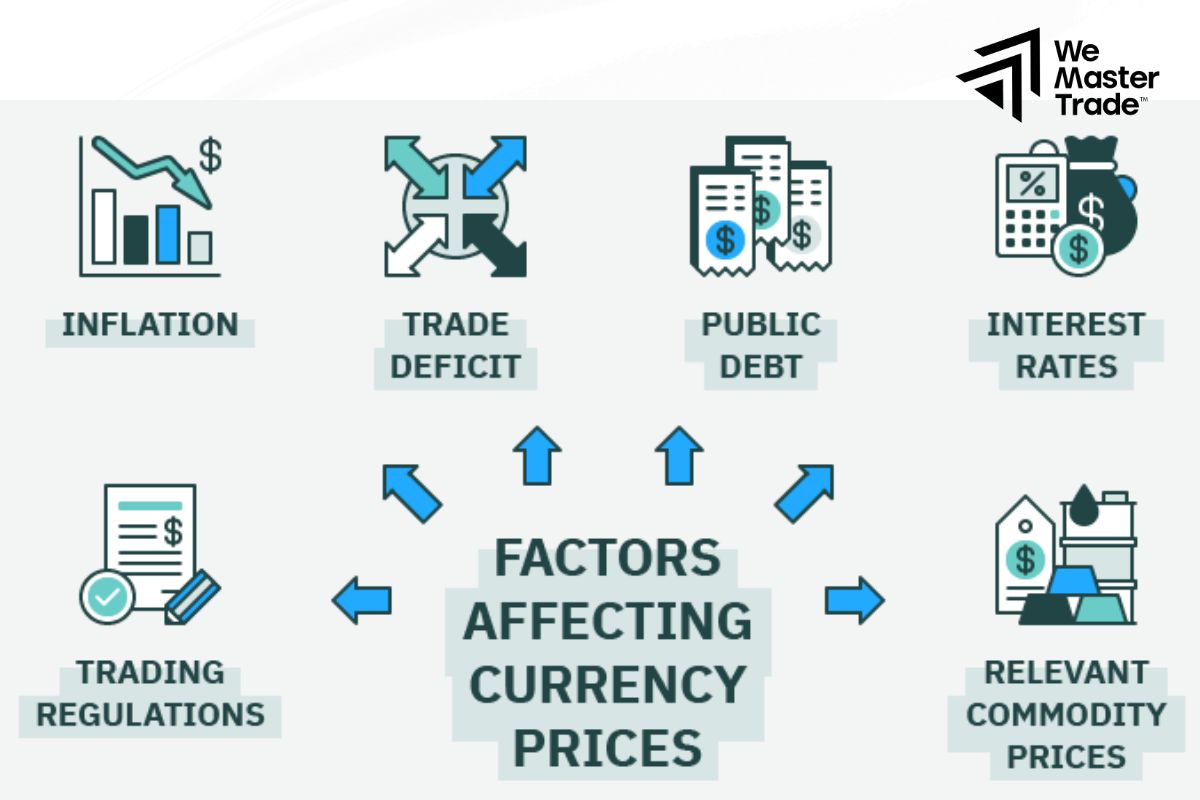
Several key factors influence Foreign Currency Effects, shaping how exchange rate fluctuations impact businesses, investments, and the broader economy. Understanding these factors is crucial for effectively managing currency risks.
- Economic Indicators: Inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth affect currency strength.
- Political Stability: Stable governments and policies attract investment, boosting currency value.
- Market Speculation: Trader perceptions and speculation drive short-term currency changes.
- Trade Balances: Surpluses strengthen currencies; deficits weaken them.
- Global Events: Crises, wars, and commodity price shifts impact currency values.
- Central Bank Actions: Interest rate changes and market interventions influence exchange rates.
- Foreign Investments: High FDI inflows signal economic confidence, strengthening the currency.
How Foreign Currency Effects Impact Different Sectors
Foreign Currency Effects influence various sectors differently, shaping their profitability, costs, and competitiveness. Here’s how they impact key industries:
Export and Import Businesses

- A weaker domestic currency makes exports cheaper and more competitive internationally, boosting sales.
- A stronger domestic currency reduces costs for imported goods but increases the expense of exports.
Tourism and Hospitality
- A weaker currency attracts international tourists by making travel and services more affordable, boosting revenues.
- A stronger currency may deter foreign visitors and increase the cost for locals traveling abroad.
Manufacturing
- Manufacturers reliant on imported raw materials face higher costs when the domestic currency weakens.
- Export-oriented manufacturers benefit from a weaker currency, increasing global competitiveness.
Financial Sector

- Exchange rate fluctuations impact investments, loans, and international transactions.
- Banks and financial institutions often face increased volatility in foreign-denominated portfolios.
Retail and E-commerce
- Retailers dependent on imported goods experience higher costs with a weaker currency, potentially reducing profit margins.
- Export-focused e-commerce platforms gain from a weaker domestic currency, enhancing affordability for international customers.
Energy and Commodities
- Countries reliant on energy imports (like oil) face rising costs with a weaker currency, affecting production expenses.
- Commodity exporters benefit from favorable exchange rates, increasing revenues.
Real Estate

- A weaker currency attracts foreign investors seeking discounted property prices, boosting demand.
- Strong currencies may discourage international investments in domestic real estate.
Managing Foreign Currency Effects
For Businesses
- Lock in exchange rates for future transactions to mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations.
- Source raw materials or products from multiple countries to reduce dependency on one currency.
- Negotiate contracts in stable or mutually agreed currencies to manage volatility.
For Investors
- Trade in Forex to hedge against potential losses in other investments caused by currency depreciation.
- Focus on currencies of stable economies or those with growth potential for long-term gains.
- Opt for funds designed to mitigate foreign currency risks, particularly in international investments.
- Evaluate costs and benefits of hedging to align with investment goals.
For Policy Makers

- Intervene in foreign exchange markets to correct short-term volatility.
- Maintain reserves of foreign currencies to ensure liquidity and investor confidence.
- Use interest rate adjustments to influence currency strength.
- Employ fiscal measures such as budgetary changes to support economic stability and address currency effects.
Foreign Currency Effects Example
A U.S.-based company, GlobalTech Inc., exports electronic components to Europe and imports raw materials from Japan.
Revenue from European Sales
- GlobalTech Inc. exports products to Europe and receives payments in euros (EUR). If the EUR/USD exchange rate changes unfavorably (e.g., the euro weakens against the dollar), the value of their revenue in U.S. dollars will decrease.
- Example: If the current exchange rate is 1 EUR = 1.10 USD, and GlobalTech Inc. sells 1 million EUR worth of products, it receives 1.1 million USD. However, if the euro weakens to 1 EUR = 1.05 USD, the same 1 million EUR will now convert to only 1.05 million USD, resulting in a loss of 50,000 USD.
Importing Raw Materials from Japan
- GlobalTech Inc. also imports raw materials from Japan and pays in yen (JPY). If the Japanese yen strengthens against the dollar (e.g., the USD weakens), the cost of raw materials in U.S. dollar terms increases.
- Example: If the current exchange rate is 1 USD = 110 JPY, and the company purchases 10 million JPY worth of raw materials, the cost in USD is approximately 90,909 USD. However, if the yen strengthens to 1 USD = 105 JPY, the same 10 million JPY costs about 95,238 USD, increasing the company’s costs by 4,329 USD.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Foreign Currency Effects is crucial for businesses and individuals navigating global markets. These effects can significantly impact your financial decisions, from exchange rate fluctuations to international investments. By staying informed and employing effective strategies, you can minimize risks and capitalize on opportunities. Stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions today!
See more:











