Have you ever wondered how much money you will lose if the stock market drops? Risk is inevitable when deciding to trade investments in a volatile market environment. Analyzing and managing Market Risk is one of the leading solutions to help minimize potential losses and increase the chance of success in investing. Let’s explore the secret to minimizing risks right below:
What Is Market Risk?

Market risk is the possibility that the value of your investments will be affected and reduced by general fluctuations in the market. Financial markets are always changing, sometimes up, sometimes down. These fluctuations can be due to many different reasons, such as:
- Changes in interest rates: When banks increase interest rates, many people will transfer money from stocks to savings, causing stock prices to decrease.
- Exchange rate fluctuations: If your country’s currency weakens compared to other currencies, the value of your investments in other currencies will also decrease.
- Unexpected events: Events such as war, economic crisis, epidemic… can cause the market to fluctuate.
Market risk affects almost all types of investments, from stocks, bonds to commodities.
See now:
- Tips Simplify Your Financial Risks Management Process
- Financial Risk Assessment, Identification and Management
- What is interest rate risk? How to manage interest rates
Types of Market Risk
To make it easier to identify, Market Risk are divided into the following four main types:
Interest rate risk

Interest rate risk can vary depending on the type of asset and the geographical area in which you invest. When interest rates increase or decrease suddenly, financial markets often become more volatile because interest rates directly affect the spending and investment decisions of both people and businesses. Specifically:
- Increasing interest rates: If banks increase interest rates, people will tend to save more and spend less. Businesses will also limit borrowing for investment, leading to reduced production and profits. This can cause stock prices to fall.
- Declining interest rates: On the contrary, when interest rates decrease, people will tend to spend more and borrow money to buy houses and cars. Businesses will also find it easier to borrow money to expand production. This often stimulates economic growth and increases stock prices.
Stock price risk
Stock price risk is the possibility that the value of the stocks you own may decrease significantly in a short period of time due to unusual fluctuations in the market.
There are many reasons why stock prices change, from news about the company, the general economic situation to unexpected events in the market. Stock price risk can be divided into two main types:
- Systematic risk: This is a risk that affects the entire market, like when the entire stock market falls. For example, when there is a global economic crisis, the prices of most stocks fall.
- Specific risk: This is a risk that is only related to a specific company. For example, if a company is sued or has a problem with its product, only that company’s stock price is affected.
Exchange rate risk

Exchange rate risk is the possibility that the value of your investment or transaction will change due to fluctuations in exchange rates between currencies. To put it simply, when you travel to Japan and exchange 1 million VND for Yen. If the Yen increases in value compared to the Vietnamese Dong, when you return home, the remaining Yen will be exchanged for less Vietnamese Dong. This risk occurs when:
- The exchange rate between currencies is not fixed but always fluctuates due to economic, political, inflationary situations, etc.
- The exchange rate changes, the value of income and expenses in foreign currencies also changes.
Commodity price risk
The possibility that the prices of commodities such as oil, gold, coffee, or even corn fluctuate strongly and are difficult to predict. These fluctuations can occur due to many different reasons such as:
- Extreme weather: Droughts, storms and floods can reduce agricultural production, pushing prices up.
- Political fluctuations: Wars, conflicts, and new government policies can all affect the supply and price of goods.
- Changes in demand: When demand for a good increases, its price will also increase.
Commodity price risk affects not only those who directly trade the goods, but also the entire economy.
For example, the stock prices of companies that produce goods will fluctuate with the prices of those goods.
How to analyst and measure market risk
To predict and measure risks occurring in the market, investors often rely on two main tools:
Value at Risk (VaR)
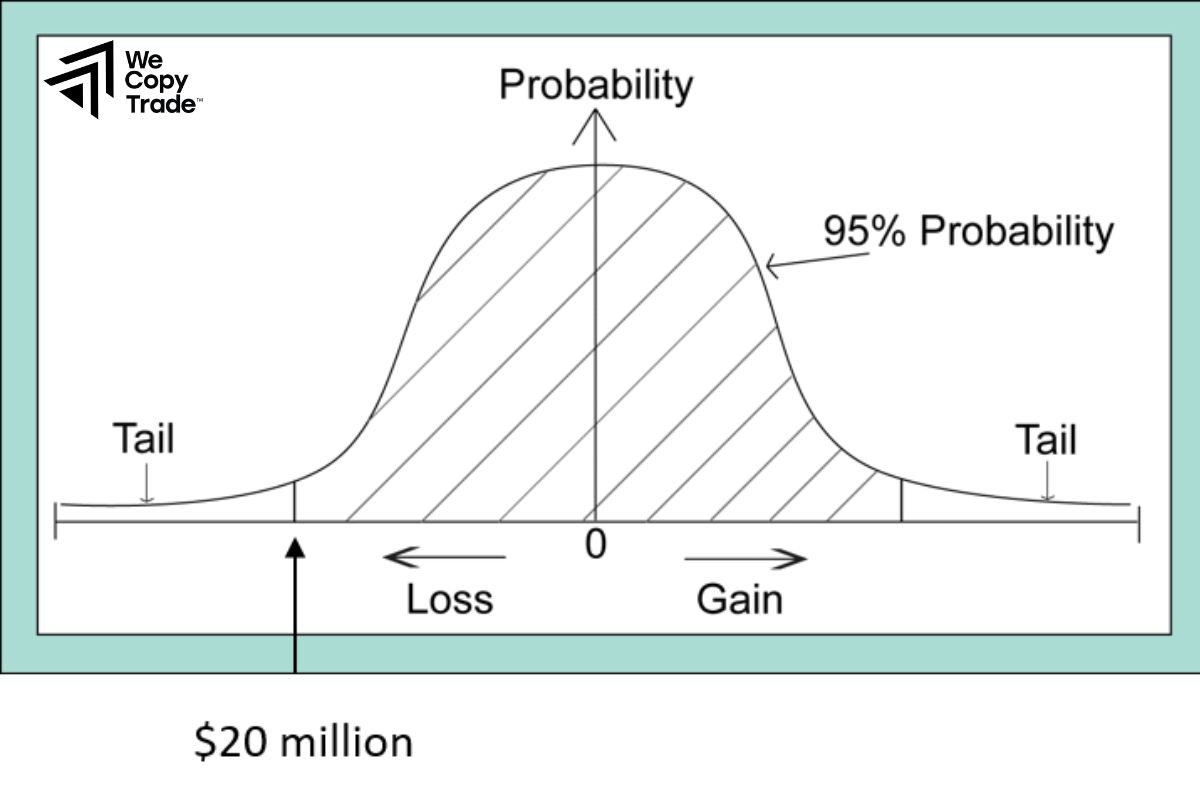
Value at Risk is a tool used by investors to forecast risks in investing. Simply put, VaR indicates the maximum loss that a portfolio can withstand over a certain period of time with a certain level of confidence.
For example, if the VaR of a portfolio is 1 million VND with a 95% confidence level, it means that there is a 95% chance that the portfolio will not lose more than 1 million VND over a specific period of time.
There are many methods to calculate VaR, but the two most common methods are:
- Historical method: based on historical data on the portfolio’s returns combined with analysis of past results, we can estimate the probability of different levels of loss occurring in the future. However, this method assumes that the future will be similar to the past, which is not always true.
- Parametric method: This method is based on the assumption that the returns of the portfolio follow a specific probability distribution, usually a normal distribution. By using statistical information such as the mean and standard deviation, we can calculate VaR. However, this method may not be accurate if the actual returns do not follow a normal distribution.
Equity Risk Premium (ERP)
When you invest in stocks, you will face more risk than when you put your money in a bank. Stock prices can fluctuate, and may even lose all their value. To encourage people to invest in stocks, the market will pay investors a higher return than safe investments. The return that comes with this risk ratio is the ERP.
How to calculate ERP:
- Expected return: This is the return that investors expect to receive when investing in the stock market.
- Risk-free rate: This is the return that you can receive from safe investments such as government bonds, without the risk of losing capital.
- ERP = Expected return – Risk-free rate
Unlike MRP – the compensation for the risk of investing in many different types of assets; ERP only focuses on the risk of investing in stocks.
How to Mitigate and Manage Your Market Risk

Measuring risk is just the first step. It is important to take specific actions to control risk. Risk control measures often include:
- Setting limits for each type of risk, ensuring that the allowable threshold is not exceeded.
- Diversifying the investment portfolio to reduce the risk of concentration in a certain type of asset.
- Using derivatives to hedge or speculate.
- Reviewing and adjusting the investment portfolio, monitoring and evaluating regularly and continuously.
Conclusion
In conclusion, market risk is an integral part of investing. Understanding this risk will help you make better investment decisions and better protect your assets. Hopely, this article can help you have a good strategy in mitigating the market risks. Good luck!
See more:











