Manual trading puts you in the driver’s seat of your financial decisions. Unlike automated systems, trading is all about analyzing the market yourself, interpreting trends, and making decisions based on your own insights. It’s a strategy that gives you the freedom to adjust and adapt, allowing you to act on real-time data and your intuition. Ready to take charge of your trades and make informed decisions? Discover the power of manual trading and start investing with confidence today!
What is Manual Trading?

Manual trading is the process of buying and selling financial assets, such as stocks, currencies, or commodities, based on a trader’s own analysis and judgment. Unlike automated trading systems that rely on pre-set algorithms, manual trading requires a hands-on approach. Traders manually analyze market data, study charts, follow trends, and make decisions on when to enter or exit trades.
This method allows for greater flexibility and a personal touch, as traders can quickly adapt their strategies to changing market conditions. While it requires more time and effort, manual trading offers the advantage of making informed decisions tailored to each unique situation, giving traders full control over their investments.
See more:
- Resolving Brokers Disputes Process with the CySEC licensed
- What is the National Futures Association? NFA license broker
- How to claim about Fraudulent Trading Practices at CFTC
- Guide How To Check And Choose FSCA Regulated Brokers
Characteristics of Manual Traders
Manual trading often shares a unique set of characteristics that set them apart from algorithm-driven or automated traders. Here are some of the key traits commonly found in successful manual traders:
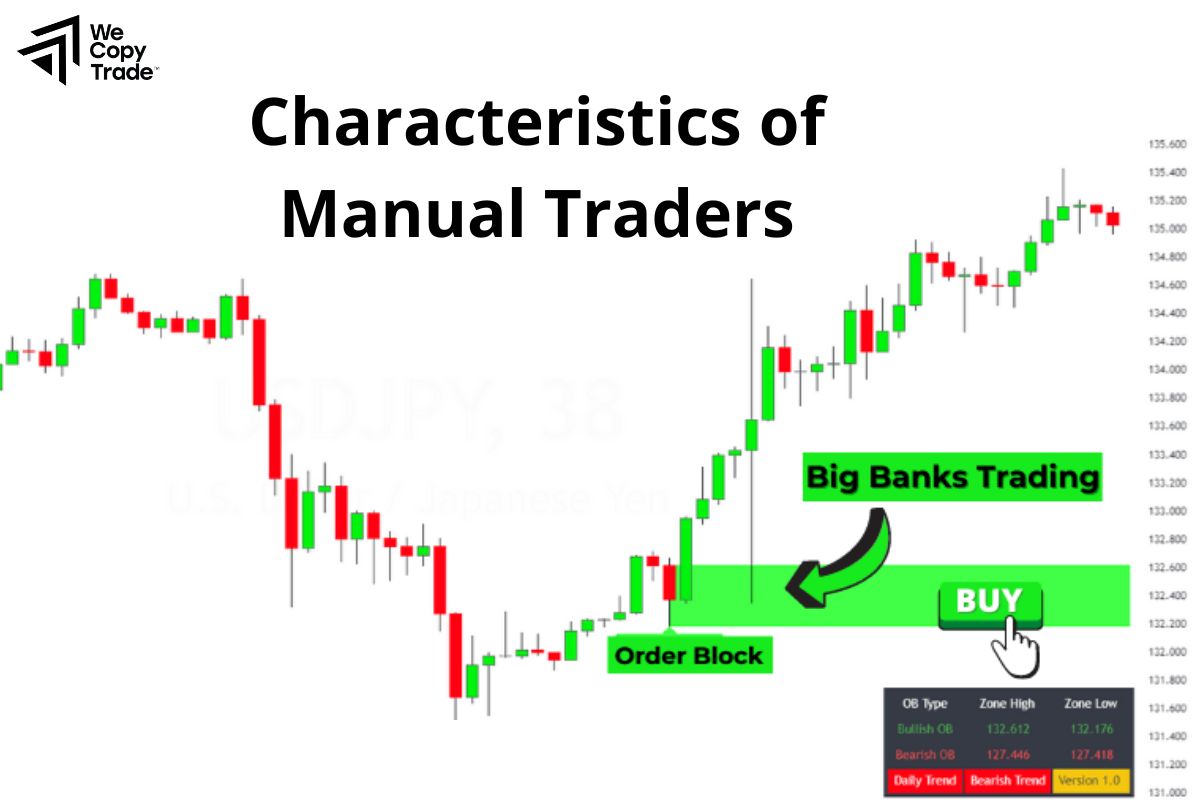
Analytical Skills
Manual traders are adept at analyzing market trends, reading charts, and interpreting technical indicators. They rely heavily on data and their ability to understand patterns in price movements.
Patience and Discipline
Successful manual traders are patient, waiting for the right moment to execute trades. They have the discipline to stick to their strategies, even when emotions might suggest otherwise, avoiding impulsive decisions.
Market Knowledge
Manual traders often have a deep understanding of the markets they trade in. They stay updated on economic news, geopolitical events, and market sentiment, as these factors can impact their trading decisions.
Adaptability
Manual traders can quickly adapt to unexpected market changes. Unlike automated systems, they can adjust their strategies on the fly, making decisions based on real-time events.
Strong Risk Management

Good manual traders are keenly aware of the risks involved and implement strict risk management strategies. They set stop-loss orders, manage position sizes, and avoid over-leveraging to protect their capital.
Intuition and Experience
Years of experience often build a trader’s intuition—an invaluable asset in manual trading. Experienced manual traders develop a “feel” for the market, allowing them to make split-second decisions based on their gut instincts and past experiences.
Emotional Control
Manual trading requires emotional control, as market volatility can trigger anxiety or excitement. Skilled traders maintain a level-headed approach, making logical decisions rather than being swayed by emotions.
These characteristics help manual traders navigate the challenges of the financial markets, making them resilient and adaptable in the face of market unpredictability.
Manual Trading Strategies
Manual trading relies on a hands-on approach, allowing traders to craft strategies based on their own analysis, research, and market experience. Here are some of the most common strategies:
Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling assets within the same trading day. The goal is to capitalize on short-term price movements, requiring quick decisions and precise timing. Day traders often use charts and technical indicators to identify entry and exit points, taking advantage of market volatility.
Swing Trading
Swing trading focuses on capturing gains over a period of days or weeks. Swing traders aim to profit from price swings in the market, often holding positions for several days to ride out short-term trends. They rely heavily on technical analysis, chart patterns, and momentum indicators to make informed decisions.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders aim to make small profits from numerous trades throughout the day. Scalpers take advantage of tiny price fluctuations and aim to exit positions quickly often within minutes or even seconds. This strategy demands excellent timing, market insight, and fast decision-making.
Trend Following

Trend following involves identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing market trend, whether it’s upward or downward. Traders using this strategy look for confirmed trends and aim to ride them as long as possible. They often use moving averages, trendlines, and momentum indicators to spot and confirm trends.
Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. This strategy focuses on fundamental analysis, taking into account economic data, industry trends, and company performance. Position traders are less concerned with short-term fluctuations and instead focus on the bigger picture.
Counter-Trend Trading
Counter-trend trading involves going against the prevailing market trend. Traders using this strategy look for overbought or oversold conditions, aiming to capitalize on price reversals. This strategy requires strong analytical skills, as predicting when a trend will reverse can be challenging.
Price Action Trading
Price action trading focuses on reading raw price movement without relying heavily on indicators. Traders analyze candlestick patterns, support and resistance levels, and chart formations to make decisions. This strategy emphasizes simplicity and understanding of market behavior.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Traders
Manual trading has its own unique strengths and weaknesses. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages to help you decide if manual is the right approach for you:

Advantages of Manual Trading
- Manual trading allows you to make your own decisions based on real-time analysis, giving you complete control over your trades. Unlike automated systems, you can quickly adjust your strategy based on market changes, news, or sudden price movements.
- Manual traders can adapt to unexpected events or market conditions on the fly. You have the flexibility to enter or exit trades based on your intuition, experience, or gut feeling, without being confined by automated rules.
- You can tailor your trading strategy to fit your unique goals, risk tolerance, and market understanding. This personalization allows you to fine-tune your methods as you gain more experience and learn what works best for you.
Disadvantages of Manual Trading
- Emotional bias can be a significant drawback in manual trading. Fear, greed, or stress can influence your decisions, leading to impulsive trades or the temptation to hold onto losing positions longer than necessary.
- Unlike automated trading, manual trading does not allow you to execute trades 24/7 without supervision. You need to be actively involved, meaning missed opportunities could occur when you’re not available to monitor the market.
- Manual trading is susceptible to human errors, such as incorrect data input, misjudging trends, or ignoring crucial market signals. These errors can lead to significant losses, especially if proper risk management is not in place.
Difference between automated and manual trading
Automated and manual trading are two distinct approaches to executing trades in financial markets. Here’s a detailed comparison of the two:

| Aspect | Manual Trading | Automated Trading |
| Decision-Making | Based on personal analysis and intuition | Follows pre-programmed algorithms and rules |
| Speed | Slower due to manual execution | Fast and efficient with instant execution |
| Control | Full control over each trade | Limited control, as trades are automated |
| Emotions | Prone to emotional decisions | Emotion-free, as trades follow strict logic |
| Flexibility | Can adapt quickly to unexpected events | Less adaptable, tied to pre-set conditions |
| Time Investment | Requires active monitoring and time | Can run 24/7 without constant supervision |
| Learning Curve | Involves continuous learning and market engagement | Requires understanding of algorithms and programming (optional) |
| Risk of Human Error | Higher, due to manual input and emotional influence | Lower, but technical errors or glitches can occur |
Conclusion
In conclusion, manual trading offers a unique advantage by putting you in complete control of your investment decisions. It allows for flexibility, adaptability, and a personalized approach to navigating the markets. If you’re ready to take your trading to the next level, sharpen your skills, and start making informed, calculated decisions, it’s time to embrace the world of manuals. Start your journey today and take control of your financial future!











