Interest rate risk is the potential loss of investment value due to changes in interest rates. To protect your assets, it is essential to understand how changing interest rates impact your portfolio and employ strategies such as diversification and hedging. Therefore, to better understand how to manage interest rates most effectively, follow the article below to start managing your interest rate risk today!
What Is Interest Rate Risk?

Interest rate risk is the potential for financial loss resulting from changes in interest rates. It affects investments, loans, and other financial instruments, especially those with fixed or variable interest rates. When interest rates rise or fall, the value of assets like bonds or loans can fluctuate, impacting an investor’s or institution’s financial performance.
However, managing interest rate risk involves using strategies like diversification, hedging, or adjusting the duration of interest-sensitive assets.
See more:
- Tips Simplify Your Financial Risks Management Process
- Financial Risk Assessment, Identification and Management
- Some Steps to Successful Liquidity Risk Management 2024
Example of Interest Rate Risk
An example of interest rate risk can be seen in bond investments:
Suppose you own a 10-year bond that pays a fixed interest rate of 3% annually. If interest rates in the broader economy rise to 5%, the bond you hold becomes less attractive to potential buyers, as newer bonds are offering a higher return. As a result, the market value of your bond decreases. If you try to sell it before maturity, you would likely have to sell at a lower price, resulting in a loss.
This illustrates interest rate risk, the risk that changes in interest rates will negatively affect the value of your investments. Investors often face this risk with fixed-income securities, especially in a rising interest rate environment.
Types of Interest Rate Risk
There are several types of interest rate risk that can affect investments and financial instruments. These include:
Price Risk (Market Risk)
This occurs when changes in interest rates impact the market value of fixed-income securities like bonds. For example, rising interest rates cause existing bonds with lower rates to lose value since new bonds offer higher returns.
Reinvestment Risk
This risk arises when interest rates fall, and an investor must reinvest interest payments or the principal from matured investments at lower rates, reducing potential earnings. This is common with short-term investments or bonds that are regularly reinvested.
Yield Curve Risk
This risk happens when interest rate changes affect different maturities along the yield curve unevenly. For example, short-term and long-term interest rates may shift differently, affecting the value of bonds or other securities based on their duration.
Basis Risk
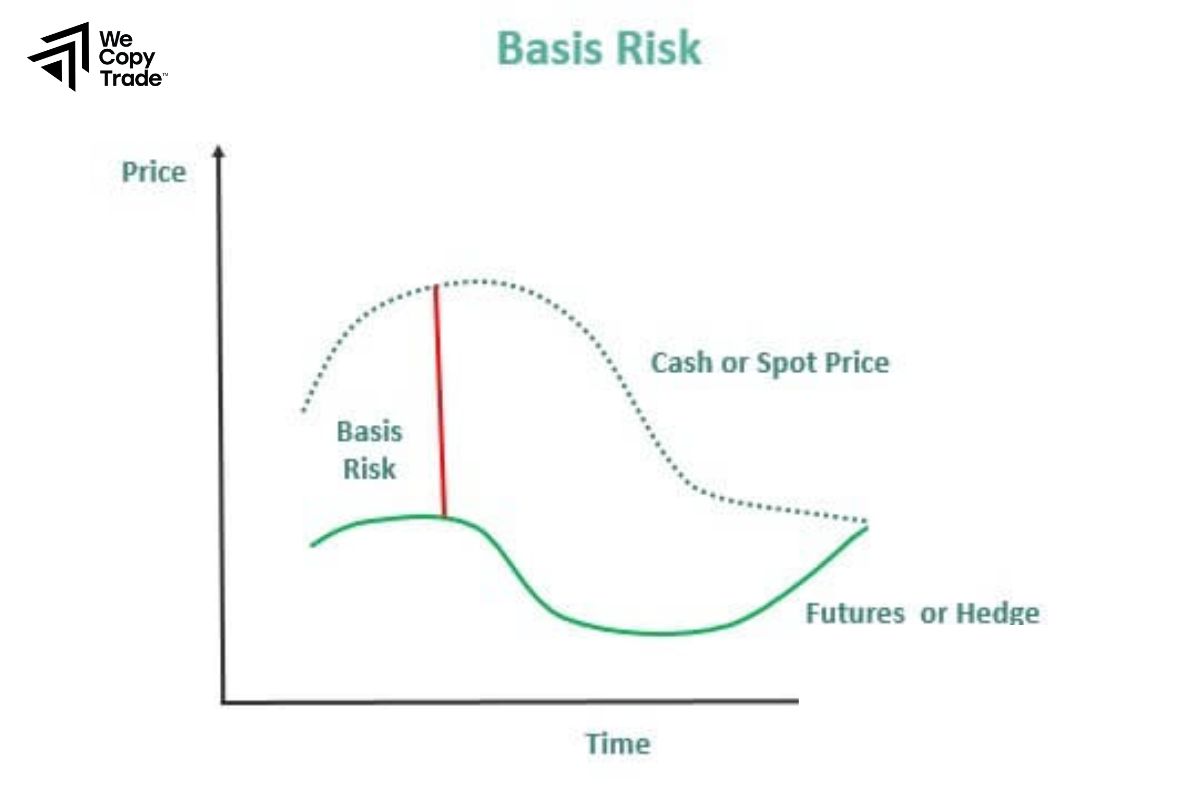
Basis risk refers to the risk that interest rates on different financial instruments may move in different directions or by different amounts. This is common when using hedging strategies like interest rate swaps, where mismatches between rates can occur.
Call Risk
This occurs when an issuer of a callable bond decides to repay the bond before its maturity, usually when interest rates fall. The bondholder must then reinvest the returned principal at a lower rate, leading to lower returns.
Duration Risk
This refers to the sensitivity of a bond’s price to changes in interest rates. Bonds with longer durations are more sensitive to rate changes and face greater interest rate risk.
How to Manage Interest Rates Effectively
To manage interest rate risk effectively, you can apply a few simple but highly useful methods. Here are some ways to protect your investments from interest rate fluctuations:
Diversify your investments
Instead of putting all your eggs in one basket, spread your money across different assets like stocks, bonds, and real estate. When interest rates change, some assets may lose value, but others can balance that out, keeping your returns stable.
Manage bond durations
Short-term bonds are less affected by rising interest rates, while long-term bonds are more sensitive. If you’re investing in bonds, consider adjusting the duration to reduce your risk.
Use hedging tools
Tools like interest rate swaps, futures, or options can help you protect your investments from unexpected changes in interest rates. However, this approach is usually more suited for professional investors.
Bond ladder strategy
Invest in bonds with different maturity dates, known as a “bond ladder,” which gives you more flexibility when reinvesting as interest rates change. When one bond matures, you can reinvest at a new rate, avoiding getting stuck at a low rate.
Mix fixed and floating rates
Consider investing in both fixed-rate and floating-rate bonds. Floating-rate bonds adjust as interest rates change, while fixed-rate bonds offer stability when rates fall.
Use interest rate caps and floors
If you have a loan with a variable interest rate, you can request a rate cap or floor. This limits how much your interest rate can rise, helping you avoid sudden rate hikes.
Stress test scenarios
For businesses or larger investors, simulating bad scenarios (stress testing) when interest rates change helps you anticipate risks and prepare a timely response.
Factors that affect Interest Rate Risk
Several factors influence interest rate risk, impacting how changes in interest rates can affect investments and financial instruments. Here are some key factors to consider:

- Economic Conditions: Higher inflation typically leads to increased interest rates, as central banks raise rates to control inflation. This can negatively impact the value of fixed-income securities.
- Central Bank Policies: Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the U.S., set benchmark interest rates that influence overall market rates. Changes in monetary policy, such as rate hikes or cuts, can significantly affect interest rate risk.
- Market Demand and Supply: The supply and demand for credit and investments play a crucial role in determining interest rates. High demand for loans can push rates up, while increased supply of bonds can lower rates.
- Maturity of Securities: The longer the maturity of a bond or loan, the more sensitive it is to interest rate changes. Long-term securities face greater interest rate risk compared to short-term securities, which are less affected.
- Credit Risk: Changes in the perceived creditworthiness of borrowers can influence interest rates. If a borrower is deemed riskier, lenders may demand higher interest rates to compensate for that risk, affecting the overall interest rate environment.
- Global Events: Geopolitical events, financial crises, and international economic developments can influence interest rates worldwide. For example, uncertainties in the global market can lead to volatility in interest rates.
- Investor Behavior: Changes in investor sentiment and preferences can affect interest rates. For instance, if investors shift their preferences toward safer assets, demand for bonds may rise, influencing rates.
FAQ about Interest Rate Risk
Here’s a frequently asked questions (FAQ) section about interest rate risk to help clarify common inquiries:
Are there tools to hedge against interest rate risk?
- Yes, financial instruments such as interest rate swaps, futures, and options can be used to hedge against interest rate risk. These tools help mitigate potential losses due to rate fluctuations.
Can central bank policies impact interest rate risk?
- Yes, central bank policies play a significant role in influencing interest rates. Changes in monetary policy, such as rate hikes or cuts, directly affect borrowing costs and the yield on fixed-income investments, impacting interest rate risk.
What is duration, and how does it relate to interest rate risk?
- Duration measures a bond’s sensitivity to interest rate changes. The longer the duration, the more susceptible the bond is to interest rate fluctuations. Managing duration in a bond portfolio can help mitigate interest rate risk.
Conclusion
In conclusion, interest rate risk is a significant factor that can impact your investment strategy and financial health. Don’t let interest rate fluctuations catch you off guard. Take proactive steps today to mitigate this risk and secure your financial future. For expert guidance on managing interest rate risk, contact us now and start making informed financial decisions!
See now:











