Unlock the Power of Hedging to Safeguard Your Investments! In today’s volatile financial markets, understanding hedge is essential for investors seeking to minimize risks and protect their portfolios. Hedging is a strategic approach that allows you to offset potential losses by taking opposing positions in related assets, offering a safety net against market fluctuations. Ready to take control of your investments? Explore our comprehensive guide on hedge and start implementing effective strategies today!
What is Hedging?

Hedging is a risk management strategy used in financial markets to offset potential losses in investments. By taking an opposite position in a related asset, investors aim to reduce the impact of adverse price movements. Essentially, hedge acts like insurance, providing a safety net against market volatility.
Besides, common instruments for hedge include options, futures, and swaps, which allow traders to lock in prices or secure a predetermined rate of return.
See now:
- Tips Simplify Your Financial Risks Management Process
- Financial Risk Assessment, Identification and Management
- What is interest rate risk? How to manage interest rates
- Some Steps to Successful Liquidity Risk Management 2024
Applications of Hedging in the financial market
Hedging is widely applied in various financial markets, including:

- Equities: Investors can hedge their stock portfolios by purchasing put options, which grant the right to sell shares at a specific price. This protects against declines in stock prices.
- Commodities: Producers and consumers of commodities (like oil, wheat, or gold) use futures contracts to lock in prices and stabilize revenues or costs.
- Foreign Exchange (Forex): Businesses operating internationally hedge against currency fluctuations by using forward contracts to set exchange rates for future transactions.
- Interest Rates: Companies can hedge against interest rate fluctuations by using interest rate swaps to exchange fixed-rate payments for floating-rate ones, or vice versa.
- Cryptocurrencies: Traders in the crypto market may use derivatives to hedge against volatility in cryptocurrency prices, safeguarding their investments from sudden downturns.
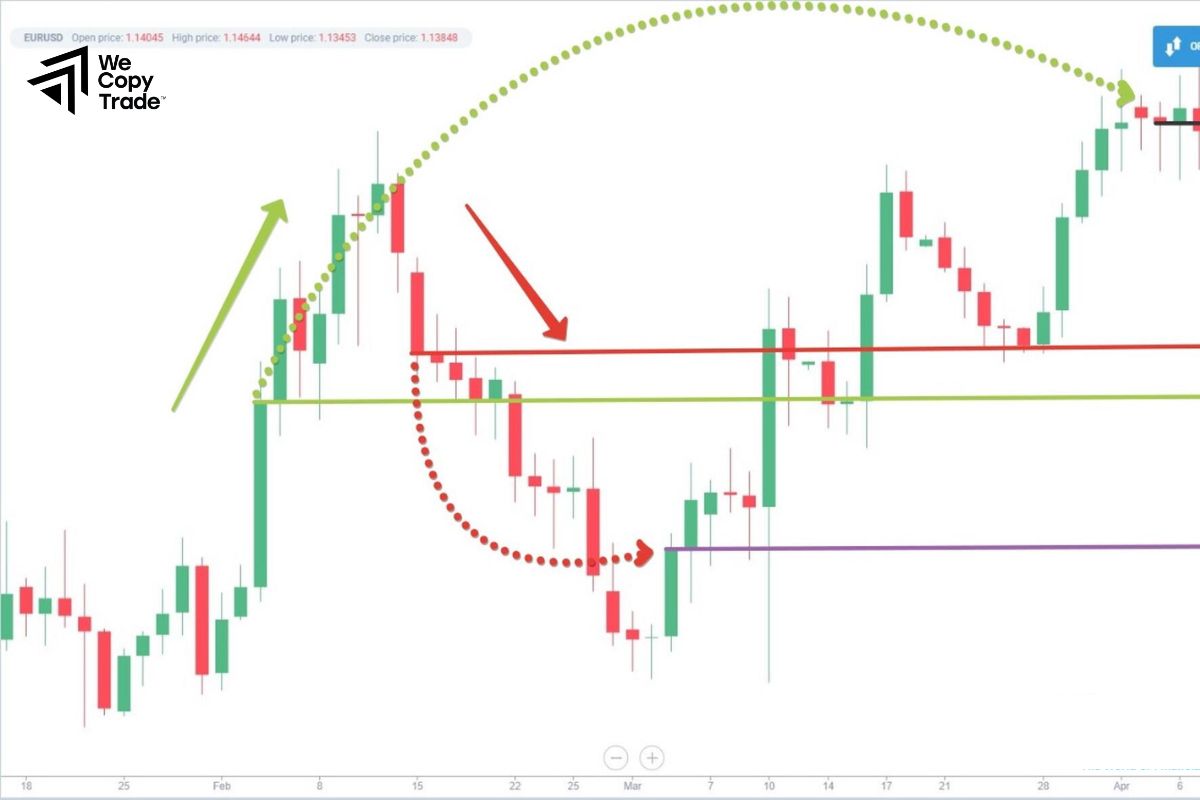
How to trade effectively with Hedging
Trading effectively with hedging requires a clear understanding of your goals, market conditions, and the various instruments available. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing a successful hedge strategy:
Hedging in Commodities
Hedging in the commodity market is an important technique that helps producers, consumers, and investors protect themselves from unwanted price fluctuations. Here are some common hedge techniques with specific numerical examples:
Using Futures Contracts
Example:
Suppose you are a corn farmer and predict that corn prices might drop before harvest. Currently, the price of corn is $5 per bushel.
- Decision: You decide to sell 100 futures contracts, with each contract representing 5,000 bushels.
- Contract Price: You sell the contract at $5 per bushel.
Outcome:
- If the price of corn drops to $4 per bushel at harvest time, you can still sell 100 contracts at $5 per bushel.
- Thus, your revenue from selling corn will be:
100 contracts × 5,000 bushels / contract × 5 USD / bushel = 2,500,000 USD - If you hadn’t sold futures contracts, you would only receive:
100 contracts × 5,000 bushels / contract × 4 USD / bushel = 2,000,000 USD
Using Options Contracts
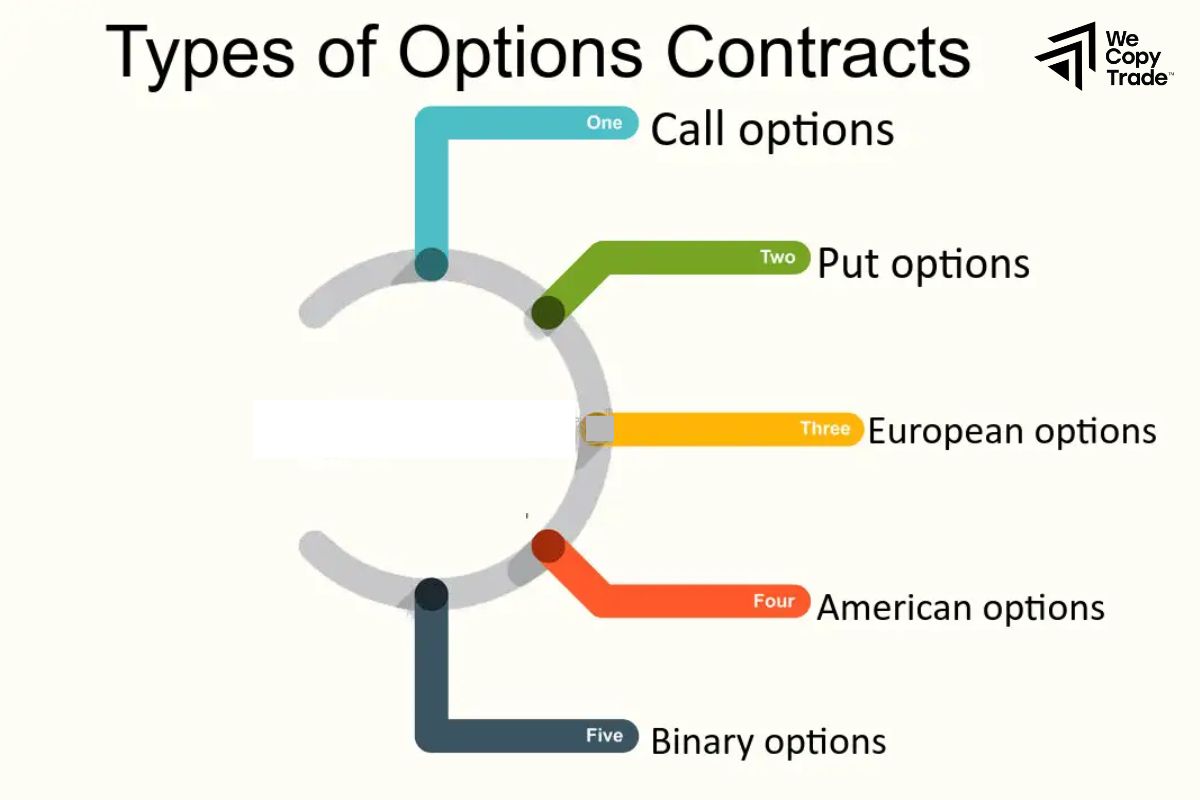
Example:
You are an edible oil processing factory and need to buy soybeans for production. Currently, the price of soybeans is $10 per bushel, but you are concerned that prices will rise.
- Decision: You buy call options for 100 contracts, with each contract representing 5,000 bushels, at an exercise price of $10 per bushel and an option premium of $0.5 per bushel.
Outcome:
- If the price of soybeans rises to $12 per bushel, you can exercise the option and buy at $10 per bushel.
Purchase Cost = 100 contracts × 5,000 bushels/contract × 10USD/bushel = 5,000,000 USD
You sell soybeans at $12 per bushel:
Revenue = 100 contracts × 5,000 bushels/contract × 12 USD/bushel =6,000,000 USD
Using Swaps
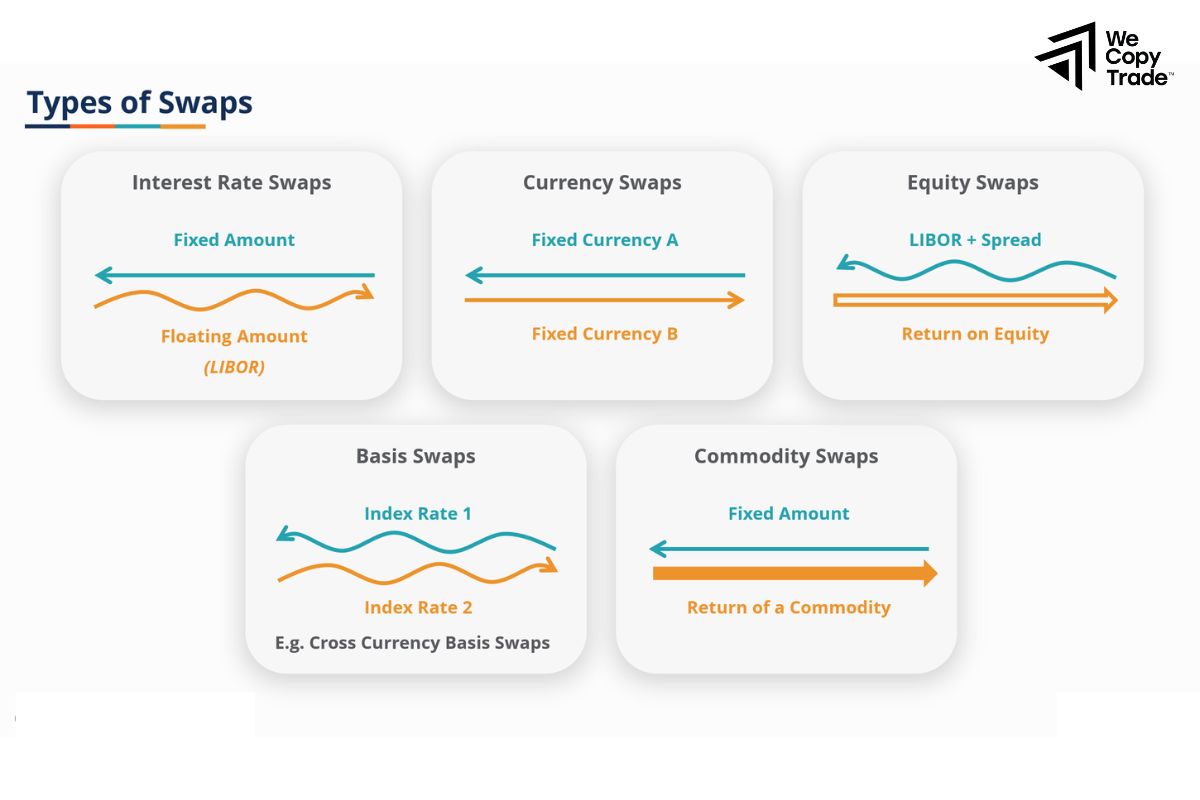
Example:
A plastic manufacturing company is concerned about price fluctuations for polypropylene. Currently, the price of polypropylene is $1,200 per ton.
- Decision: The company enters into a swap agreement with a bank, in which it will pay a fixed price of $1,250 per ton for 1,000 tons of polypropylene over 6 months.
Outcome:
- If the market price rises to $1,400 per ton, the company still pays $1,250 per ton for 1,000 tons.
Savings = (1,400−1,250) × 1,000 = 150,000 USD - Conversely, if the price drops to $1,100 per ton, the company must still pay $1,250 per ton.
Extra Cost = (1,250−1,100) × 1,000 = 150,000 USD
Hedging in Forex
Hedge in the Forex market is a strategy used to protect against unfavorable currency movements. Here are key techniques along with concise examples:
Direct Hedging
Example: If you hold a long position of 10,000 EUR in EUR/USD at 1.2000 but anticipate a decline, you can open a short position for 10,000 EUR at the same rate.
If the price drops to 1.1800:
- Long Position Loss: (1.2000−1.1800) × 10,000 = 200 USD (loss)
- Short Position Gain: (1.2000−1.1800) × 10,000 = 200 USD (gain)
Using Options
Example: As a US importer needing to pay 100,000 EUR in three months at 1.2000, you buy a put option at the same price with a 0.02 premium.
If EUR rises to 1.2500, you exercise the option:
- Cost Without Hedging: 100,000 × 1.2500 = 125,000 USD
- Cost with Hedging: 100,000 × 1.2000 + 2,000 premium = 122,000 USD
You save $3,000 by hedge.
Cross-Currency Hedging
Example: If you hold a long AUD/USD position at 0.7400 and anticipate volatility, you could hedge using NZD/USD.
Open a short position of 10,000 NZD at 0.7100. If AUD/USD drops to 0.7200:
- Long Position Loss: (0.7400−0.7200) × 10,000 = 200 AUD
- Short Position Gain: (0.7100−0.7300) × 10,000 = 200 NZD
Advantages and disadvantages of Hedging strategy

Advantages of Hedging
- Hedging significantly lowers the risk of loss from adverse price movements, providing a safety net for investors.
- It can lead to more predictable profits, allowing businesses to manage cash flow effectively.
- Various instruments and strategies allow traders to tailor hedge to their specific needs and market conditions.
- Knowing that a hedge is in place can reduce anxiety about market volatility, allowing investors to focus on long-term strategies.
Disadvantages of Hedging
- Hedging strategies can incur costs, such as option premiums or margin requirements, which may reduce overall profitability.
- Some hedge strategies can be complicated and require advanced knowledge of financial instruments and market dynamics.
- A hedge can cap potential profits if the market moves in your favor, as you may miss out on upside potential.
- Excessive hedge can lead to unnecessary losses if the hedged position moves in the opposite direction than anticipated.
Notes when using Hedging
Hedging can be a powerful tool in managing risk in trading and investments, but it’s essential to approach it with caution. Here are some key points to consider when using hedge strategies:

- Understand Your Goals: Clearly define your risk management goals and ensure your hedge strategy aligns with your overall investment objectives.
- Stay Informed: Continuously monitor market conditions and economic indicators that may affect your hedged positions.
- Diversify: Don’t rely solely on hedge; maintain a diversified portfolio to spread risk across various asset classes.
- Evaluate Performance: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your hedging strategies and make adjustments as necessary.
- Consult Experts: If you’re new to hedge, consider seeking advice from financial professionals who can provide insights and help you navigate complex strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hedging is an essential strategy for managing risk and protecting your investments in the ever-changing financial markets. By mastering techniques like direct hedge and options, you can mitigate potential losses and improve your trading performance. Don’t leave your investments to chance. Integrate hedge strategies into your trading plan today! Ready to learn more? Dive into our resources on hedge and start enhancing your financial success!
See more:











