The foreign exchange market is renowned for its high liquidity and 24/5 continuous operation. At the same time, the forex market volatility is more pronounced than in most other financial markets. These price swings create both opportunities and risks, depending on a trader’s approach and risk management skills.
Understanding the causes and characteristics of volatility helps you to read and analyze price movements more accurately, thereby enhancing your ability to identify and capitalize on trends.
What is Forex Market Volatility?
Volatility in forex describes the degree and speed of a currency pair’s price change over a specific period. During periods of high forex market volatility, a currency pair’s price can move hundreds of pips in just a few hours, while low-volatility periods are characterized by a much tighter trading range.
See now:
- Prop Firm Trading Techniques: From Basic to Advanced
- Qualifying for a Prop Firm: All the Skills You Need
- What is Exchange Rate? A Comprehensive Guide for Traders
- Prop Firm Career Opportunities: New Path for Modern Traders
Key Factors That Cause Volatility
- Economic indicators: GDP, inflation (CPI, PPI), unemployment rate, retail sales… can all cause strong fluctuations immediately after announcement.
- Geopolitical events: Elections, trade negotiations, military conflicts often cause investors to react quickly, causing exchange rate fluctuations.
- Market psychology: When anxiety increases, money flows often shift to safe-haven currencies such as JPY, CHF; conversely, when optimism increases, money flows to riskier assets.
- Interest rate differential: Yields between different countries can cause capital flows to shift, leading to changes in exchange rates.
Measuring Volatility
A popular tool is the ATR (Average True Range) – which measures the average of the actual fluctuations over a period of time (usually 14 periods). The higher the ATR, the higher the forex market volatility.
Most Volatile Currency Pairs
Not all currency pairs are equally volatile. Some pairs are highly volatile due to external factors or large differences between two economies.
Pairs Related to Commodities
- AUD/JPY: AUD is affected by commodity prices, JPY is a safe-haven currency, making this pair sensitive to global economic fluctuations.
- CAD/JPY: CAD is heavily dependent on oil prices, combined with JPY to create a pair with significant fluctuations.
Pairs Related to Developing Economies
- USD/ZAR: Dominated by gold prices, South African politics and economy.
- USD/TRY: Turkish Lira is often volatile due to high inflation and sudden policy changes.
What Causes Forex Market Volatility Markets
Identifying the causes helps to assess whether the volatility is short-term or long-term.
Unexpected Economic News

When data is released far from forecasts, the forex market volatility immediately. For example, a much better-than-expected US jobs report (NFP) can cause the USD to surge.
Political or Economic Crisis
Uncertainty such as Brexit, the European debt crisis, or oil price fluctuations often cause large and long-lasting changes.
Monetary Policy Changes
A sudden increase or decrease in interest rates by a central bank is often the leading cause of exchange rate fluctuations.
How to Monitor Forex Market Volatility
In a fast-changing price environment, keeping a close eye on developments helps make reasonable judgments.
Use an Economic Calendar
Keeping up with important data releases can help predict periods of high volatility. Reports such as CPI, GDP, or interest rate decisions often have a big impact.
Price Pattern Observation
Breakout patterns, pin bars or engulfing patterns appear more often during forex market volatility periods, reflecting strong sentiment from participants.
Volatility Analysis Tools and Methods
Technical Analysis
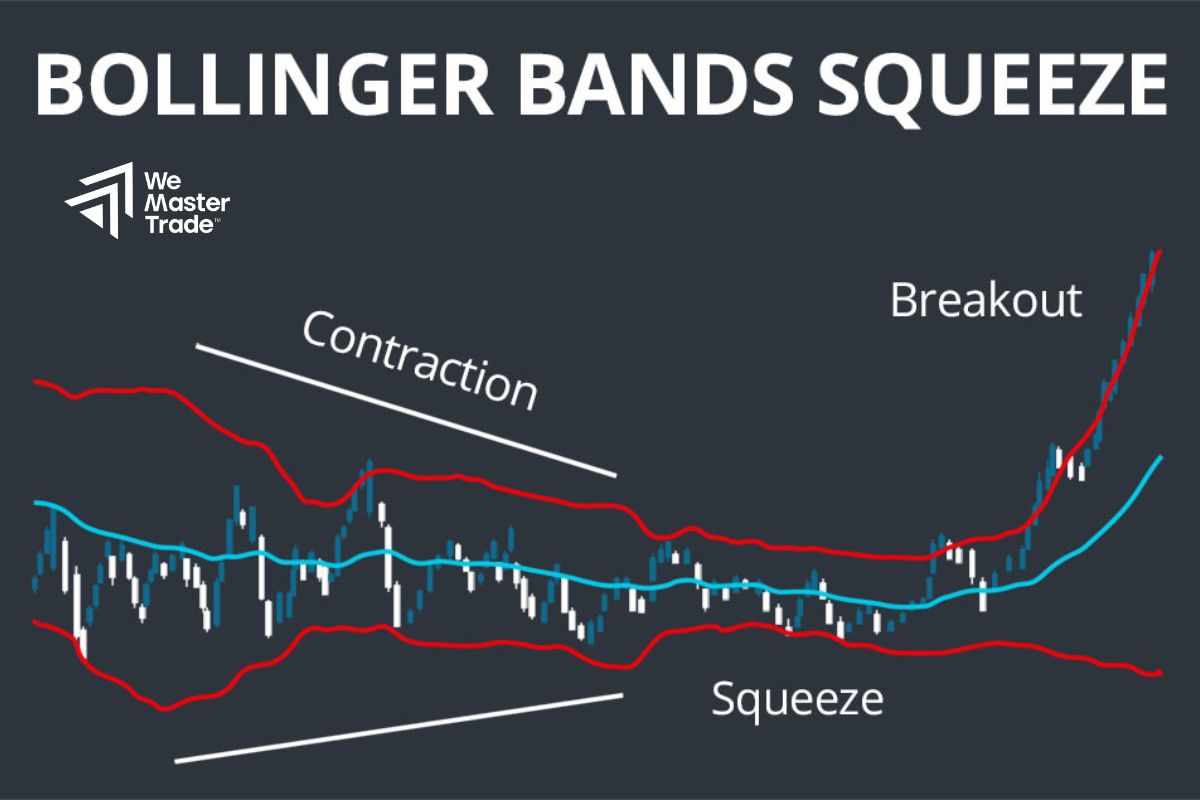
- Bollinger Bands: Helps identify when price ranges are expanding (high volatility) or contracting (sideways market). When the bands expand, it is often a signal that volatility is about to increase; conversely, when the bands narrow, the market may be preparing for a breakout.
- ATR (Average True Range): Measures the average volatility of prices over a period of time, helping traders assess risk and adjust trading volume.
- Price & Candlestick Patterns: Patterns such as triangles, pennants, or pin bars can signal a sharp change in volatility.
Fundamental Analysis
- Monitor macro factors such as economic growth, monetary policy, inflation, and political situations to predict when the forex market may move sharply.
- Economic Calendar: Stay up to date with important events such as GDP releases, NFP reports, central bank interest rate decisions, or CPI readings — these are news that often have a strong impact on exchange rates.
- Global Events: Unexpected events such as financial crises, geopolitical conflicts, or changes in trade policies can all create large and sudden movements.
Conclusion
In short, forex market volatility is a natural feature of the foreign exchange environment, influenced by a series of factors from economic and political data to market psychology. Understanding the causes, characteristics and how to monitor helps observers grasp the whole picture and avoid misinterpreting signals.
See more:











