In the dynamic world of Forex trading, the role of brokers in Forex trading is crucial as they connect traders with the global currency market. From providing essential trading platforms to offering market insights and leverage, the Brokers in Forex Trading cannot be underestimated. Choosing the right broker can make the difference between a successful trade and a missed opportunity. Ready to elevate your trading game? Explore our trusted broker recommendations and start trading with confidence today!
What is a Forex Broker?
A Forex broker is a financial services company that provides traders access to a platform for buying and selling foreign currencies. In essence, Forex brokers act as intermediaries between retail or institutional traders and the global currency market, also known as the Foreign Exchange Market or Forex.
Key Functions of a Forex Broker
- Access to the Forex Market: Forex brokers offer platforms where traders can execute trades in currency pairs, like EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, etc.
- Leverage: Brokers often provide leverage, which allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital.
- Spread: They earn profits through the spread, which is the difference between the buying (bid) and selling (ask) price of a currency pair.
- Liquidity: Brokers ensure that trades are executed efficiently by providing liquidity through connections with major banks or financial institutions.
- Trading Platforms: They offer trading software (such as MetaTrader 4 or 5) with tools like real-time charts, technical indicators, and automated trading options.
See more:
- Top Reliable Forex Brokers – How To Choose a Broker
- Top 9 Best Crypto Payments Gateways for Business 2024
- What are eWallets? Top 5 Forex eWallets you should know
Types of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers can be categorized into several types based on how they handle trades, execute orders, and interact with the Forex market. Here are the main types of Forex brokers:
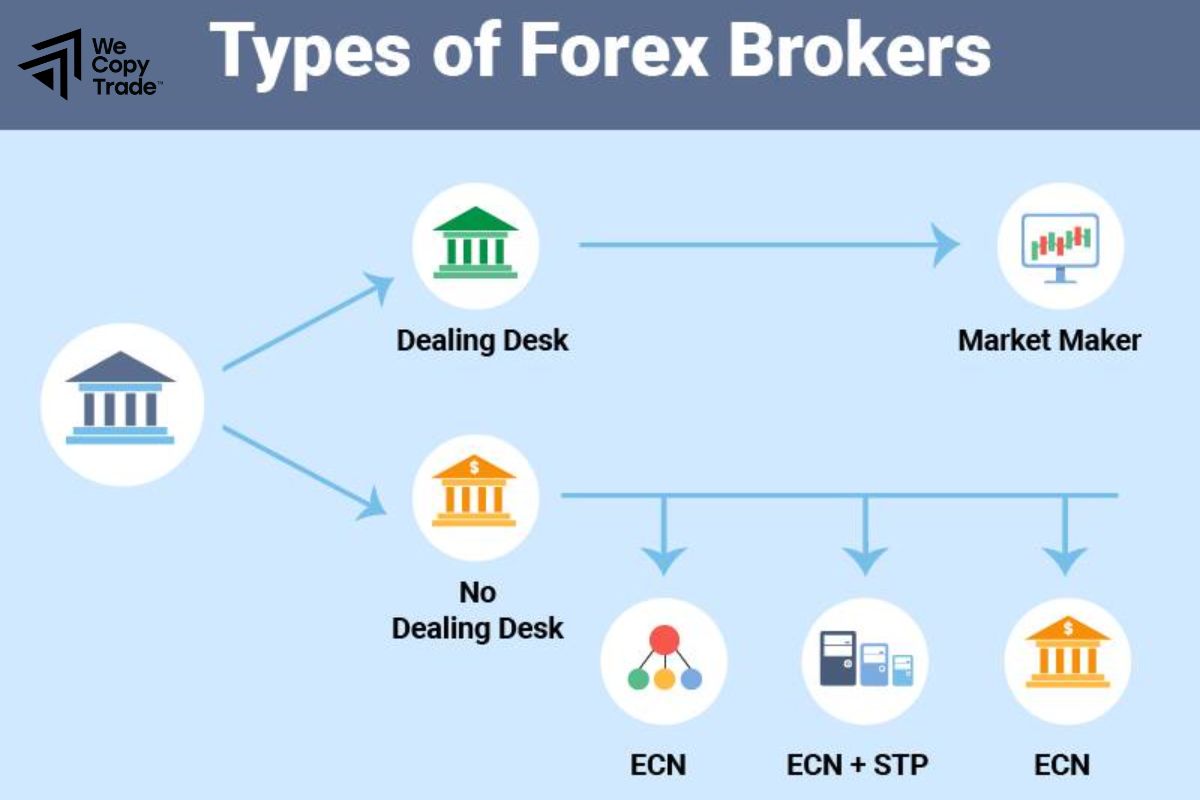
Market Maker Brokers
Market Makers create their own market for clients and act as the counterparty to trades. This means they “make” the market by setting the bid (buy) and ask (sell) prices.
- Fixed Spreads: Market Makers often offer fixed spreads, meaning the difference between the buy and sell prices remains constant regardless of market conditions.
- Counterparty to Trades: The broker takes the other side of the client’s trade. If a trader places a buy order, the broker sells, and vice versa.
- Profit from Spreads and Client Losses: They earn from spreads and, in some cases, from clients’ losses.
ECN Brokers
ECN brokers provide a direct connection between traders and the market by linking them with a network of other traders, financial institutions, and liquidity providers.
- Variable Spreads: ECN brokers usually offer variable spreads that can change based on market liquidity and volatility.
- Transparent Pricing: Since trades are routed to multiple participants, ECN brokers offer more transparent prices.
- Commission-Based: Instead of earning from spreads, ECN brokers charge a commission per trade.
STP Brokers

STP brokers send client orders directly to liquidity providers without any manual intervention, ensuring a more streamlined and faster trade execution.
- No Dealing Desk: Orders are passed directly to liquidity providers like banks, hedge funds, or other financial institutions.
- Variable Spreads: Similar to ECN brokers, STP brokers have variable spreads.
- Automatic Order Execution: Trades are executed automatically without any manual handling.
DMA Brokers
DMA brokers allow traders to directly access the order book of an exchange, showing all available buy and sell orders. Orders are matched with liquidity providers without any interference.
- Transparent Order Flow: Offers full visibility of market depth, showing where orders are being placed.
- Variable Spreads and Low Commissions: Like ECN, prices vary, but commissions tend to be lower due to direct access.
- Advanced Trading: Ideal for professional traders seeking control over order execution.
Hybrid Brokers
Some brokers combine elements of the above types, offering both Dealing Desk and No Dealing Desk services. They might act as Market Makers for smaller clients but offer ECN or STP execution for larger accounts.
- Flexible Spreads: Can be fixed or variable depending on the service offered.
- Multiple Execution Models: May switch between different types based on trade size or account type.
Role of Brokers in Forex Trading you should know
In Forex trading, a broker plays a crucial role as the intermediary that connects traders with the foreign exchange market. Here’s a breakdown of the key responsibilities and Role of Brokers in Forex Trading that you should know:

Market Access Provider
- Access to the Market: Forex brokers offer individual traders access to the global Forex market, which otherwise is primarily dominated by institutions and large financial entities.
- Trading Platform: Brokers provide the trading platforms (like MetaTrader 4 or 5) that traders use to buy and sell currencies. These platforms often come with tools for analysis, charts, indicators, and automated trading options.
Facilitating Trades
- Executing Orders: Brokers are responsible for executing the buy or sell orders placed by traders. Depending on the broker type, they may either facilitate trades between the trader and the market (Non-Dealing Desk) or trade directly against the trader (Dealing Desk).
- Order Types: They offer various order types (market order, limit order, stop-loss order, etc.), allowing traders to manage how their trades are executed.
Providing Leverage
- Access to Leverage: Brokers provide leverage, which allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This is a double-edged sword; it can magnify gains but also increase risks.
- Margin Accounts: Brokers manage margin accounts, where traders deposit funds that serve as collateral for leveraged positions. They set rules for margin requirements and may issue margin calls if necessary.
Liquidity Provider

- Ensuring Liquidity: Forex brokers ensure that there is enough liquidity for trades to be executed efficiently, even during volatile market conditions. This is critical for avoiding slippage, where an order is filled at a price different from what was requested.
- Spreads: Brokers earn money through spreads (the difference between the bid and ask price), which may vary based on market conditions and the broker’s model.
Offering Market Analysis and Tools
- Research and Analysis: Many brokers provide resources like market analysis, economic calendars, news feeds, and trading signals to help traders make informed decisions.
- Education: Some brokers also offer educational materials such as webinars, eBooks, and tutorials, aimed at helping new traders learn about Forex trading.
Regulation and Security
- Compliance with Regulations: Reputable brokers are regulated by financial authorities (like FCA, CySEC, or ASIC) to ensure transparency, security, and adherence to fair trading practices. A regulated broker gives traders confidence that their funds are safe.
- Fund Security: Brokers may offer segregated accounts to keep client funds separate from the broker’s operational funds, providing an additional layer of protection.
Customer Support
- Technical Support: Brokers provide customer support to assist with technical issues, trading platform questions, or any problems related to account management.
- Guidance: A good broker offers prompt and reliable support, often 24/7, to accommodate the global nature of Forex trading.
Choosing the Right Forex Broker
Choosing the right Forex broker is essential for successful trading. Here are the key role of brokers in Forex trading factors to consider:

- Regulation and Trust: Ensure the broker is regulated by reputable authorities like FCA, ASIC, or CySEC for safety and transparency.
- Trading Platform: Look for user-friendly platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 with essential tools, charting, and mobile access.
- Fees and Spreads: Compare spreads and commissions. Lower spreads mean lower trading costs. Watch out for hidden fees like withdrawal charges.
- Leverage and Margin: Choose a broker with leverage options that fit your risk tolerance, and check their margin requirements.
- Account Types and Minimum Deposit: Select an account type that fits your needs and ensure the minimum deposit is manageable for you.
- Customer Support: Opt for brokers with reliable 24/7 support via phone, chat, or email.
- Payment Methods: Ensure easy deposit and withdrawal options, such as bank transfers, credit cards, and e-wallets.
- Demo Account: Use a demo account to practice and familiarize yourself with the platform before trading with real money.
- Education and Research: Choose a broker that offers educational resources, market analysis, and trading tools to help you improve your skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the role of brokers in Forex trading is crucial for any trader looking to succeed in the market. Brokers provide the necessary tools, platforms, and resources to execute trades effectively while ensuring access to liquidity, leverage, and real-time market data. Explore trusted brokers who provide the best tools and customer support for successful trading.
See now:











