To have a deeper insight into the forex market, one of the important factors that affect the value of money that you need to know and distinguish clearly is debt vs. deficit. In the following article, I will help you distinguish the boundaries and the relationships between them so that you can make better investment decisions. Let’s go!
What is foreign debt?
Foreign debt is when a country borrows money from other countries, international organizations such as the World Bank or foreign investors. The amount of money that a country borrows and has not yet repaid is called foreign debt.
For example, Vietnam can borrow money from Japan to build a new bridge. The amount of money that Vietnam borrows from Japan is part of Vietnam’s foreign debt.
Normally, countries often borrow to:
- Invest in large projects such as building roads, bridges, hospitals, schools… to develop the economy.
- Overcome the consequences of natural disasters, floods
- Solve economic problems such as poverty reduction, economic growth…

See now:
- Apply The Yield Curve Effectively for Successful Trading
- Take advantages Industrial Production Index (IPI) In Trading
- Understanding Monetary Policy? Common Types of Policy
- How To Contribute A Good ISM Manufacturing Index In Trading
Effects of foreign Debt in Trading Market
National debt is like a debt that the whole country has to pay. When a country has too much debt, investors will be concerned and may not want to invest in that country anymore. This can cause the country’s currency to depreciate.
When national debt is high, the country’s currency will depreciate compared to other strong currencies. This attracts foreign investors to pour money into the real estate market, pushing up house prices. This makes it difficult for people in the country to own a house.

On the contrary, when a country has a strong economic growth and low national debt, investors will have more confidence in that economy and be willing to invest. This will increase the value of the currency.
To solve this problem, countries need to have appropriate fiscal and monetary policies to reduce public debt, stimulate economic growth and create more jobs.
Indicators to Assess a Country’s Debt Repayment Potential
To assess whether a country is “burdened” with too much debt, international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank have come up with a number of criteria. These criteria are like measuring sticks that help us know whether a country has the ability to repay all its debts.
For example, one important criterion is to compare a country’s total debt with the total value of goods that the country exports in a year. If the debt is too large compared to the value of exports, it means that the country will have difficulty repaying its debt.
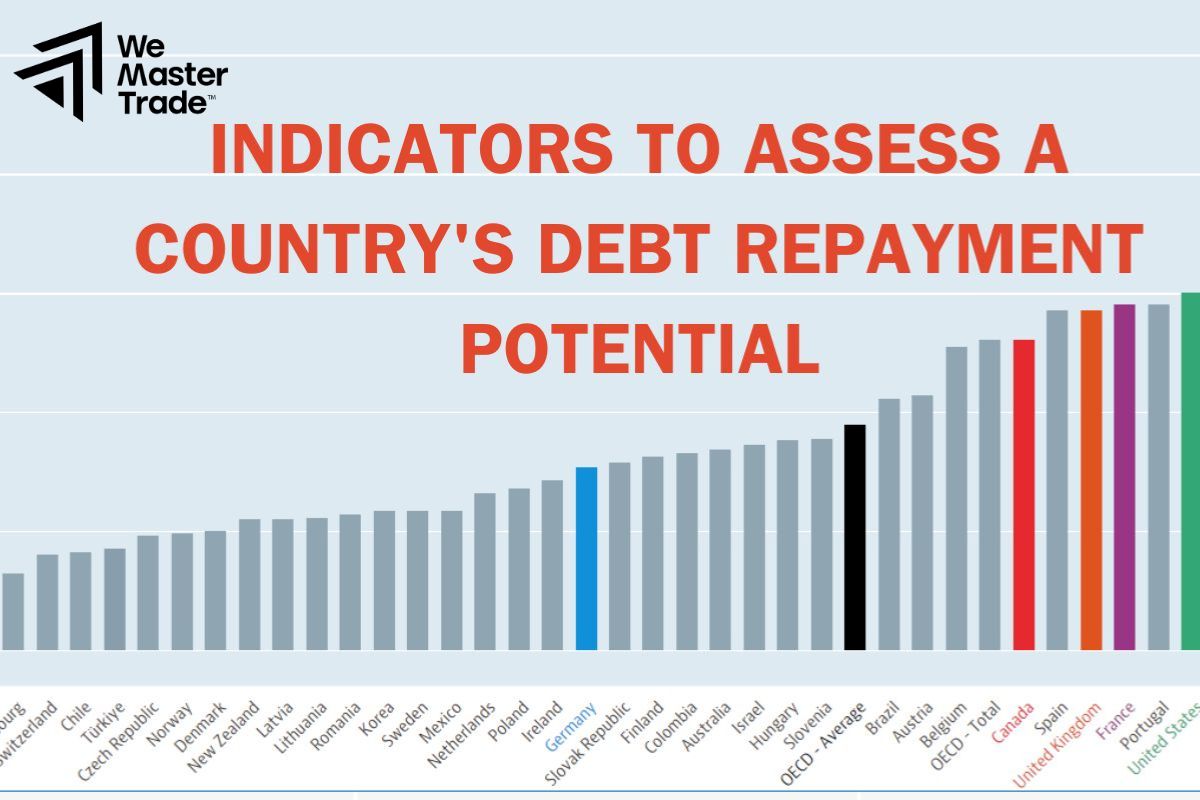
Key indicators:
- Solvency: Assesses whether a country has enough resources to repay the principal and interest in the future.
- Liquidity: Assesses a country’s ability to raise capital to repay its debts when necessary.
- Debt to GDP: Indicates the total debt burden of a country. If this number is too high, it means that the country is having difficulty paying its debts.
- Debt service: Indicates a country’s ability to pay interest each year. If this amount is too large compared to the country’s income, it will put pressure on the budget and may lead to difficulties in paying the debt.
- Outstanding debt: Indicates the structure of the debt (short-term or long-term, debt with different organizations…).
Using many different indicators helps investors have a comprehensive view of a country’s debt situation. From there, they can make accurate assessments and make appropriate decisions.
Understand about Deficit

Deficit is a situation where a country spends more on public works and social welfare than it collects in taxes, then the state budget will be in deficit. Deficit can cause inflation, increase public debt, and affect the stability of the economy. There are many causes of deficit, such as:
- When people, businesses or the government spend beyond their means.
- When the economy is difficult, income decreases, making it more difficult to balance revenue and expenditure.
- Unexpected events such as natural disasters, epidemics, and economic crises can cause deficits.
Types of deficit
Based on the subject and cause, we can divide deficits into different types:
- Budget deficit: Simply put, it means “spending more than you earn”. When the government spends on things like building roads, hospitals, paying salaries to civil servants, etc., but does not have enough tax money to pay, it is a budget deficit.
- Trade deficit: Just like a store sells less than it imports. When a country imports more goods than it exports, it will have a trade deficit.
- Revenue deficit: This is a situation where a company’s actual revenue is lower than expected. For example, a store expects to sell 100 million VND in a month but only sells 80 million VND, then they have a revenue deficit.
Understanding the types of deficits helps us assess the economic situation of a country or a business. Deficits can signal potential problems and affect the decisions of investors, governments, and people.

Debt vs. deficit Comparison
When governments run a deficit, they have to borrow to cover the shortfall. This increases the burden of national debt.
High national debt can cause inflation, increase interest rates, and reduce the country’s ability to invest and grow.
Debt vs. deficit are often confused, but they are actually quite different.
- You can think of the government as a big family. When a family spends more than it earns, it goes into debt. Similarly, when the government spends too much without getting enough tax revenue, it has to borrow money. This money is called the national debt.
- A budget deficit is when the government spends more than it earns. It is like a family spending all their savings on new furniture without any plans to pay it back later.

Key differences debt vs. deficit:
| Characteristics | Debt | Deficit |
| Origin | From borrowing from a third party | From the difference between expenditure and income |
| Debt repayment | Must pay both principal and interest | No obligation to repay debt to a third party |
| Impact | Increases financial burden, may affect credit | May lead to debt if not remedied |
| Duration | May last for years | May occur over a short or long period |
Example:
- Debt: You borrow 500 million from the bank to buy a house. You will have to pay this amount back to the bank within 20 years, along with interest.
- Deficit: A company expects to sell 100 products but only sells 80 products. This leads to a revenue deficit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, debt vs. deficit are two different but closely related concepts. Clearly distinguishing between the two will help you make smarter financial decisions. Good luck!
See more:











